Introduction to
GRASS
Helena Mitasova
and Vaclav Petras
GIS/MEA582 Geospatial Modeling and Analysis NCSU
Learning Objectives
This lecture is a brief introduction to GRASS software and overview of its features in the context of this course and open source software in general.
Open Source and Licensing
- According to Stallman (2002),
there are four freedoms that as a user you should have:
- the freedom to use the software for any purpose,
- the freedom to change the software to suit your needs,
- the freedom to share the software, and
- the freedom to share the changes you make.
Stallman, R. M. (2002). Free software, free society: selected essays. Ed. by J. Gay. 1st. ed. OCLC: 253840339. Boston, Mass: Free Software Foundation. 220 pp. ISBN 978-1-882114-98-6.
Commercial and FOSS
- FOSS can be used commercially
- FOSS can be commercial but not proprietary
- FOSS can be used to build closed platforms
- Widely used FOSS examples:
GRASS
GRASS (Geographic Resources Analysis Support System) is a Free and Open Source Software suite for geospatial data management and analysis, image processing, spatial modeling, and visualization.
GRASS
Timeline:- 1983 started at US Army CERL as land management system
- evolved into general purpose GIS
- 1999 GNU GPL, international team of developers
- 2008 OSGeo Project
- 40+ years of GRASS development

Historical Video
Historical promotional video from 1987 narrated by William Shatner
watching 1 minute is sufficient to get the idea, optionally you can watch the whole 15 minutes and see metadata and transcript at doi.org/10.5446/12963
Software Implementation
- portable:
- many operating systems: MS Windows, Mac OS, Linux, ...
- high-end desktops, low-end laptops, Raspberry Pi, High-Performance Computing clusters, ...
- single integrated software
- functionality implemented as 500+ tools (modules)
- written in C and Python
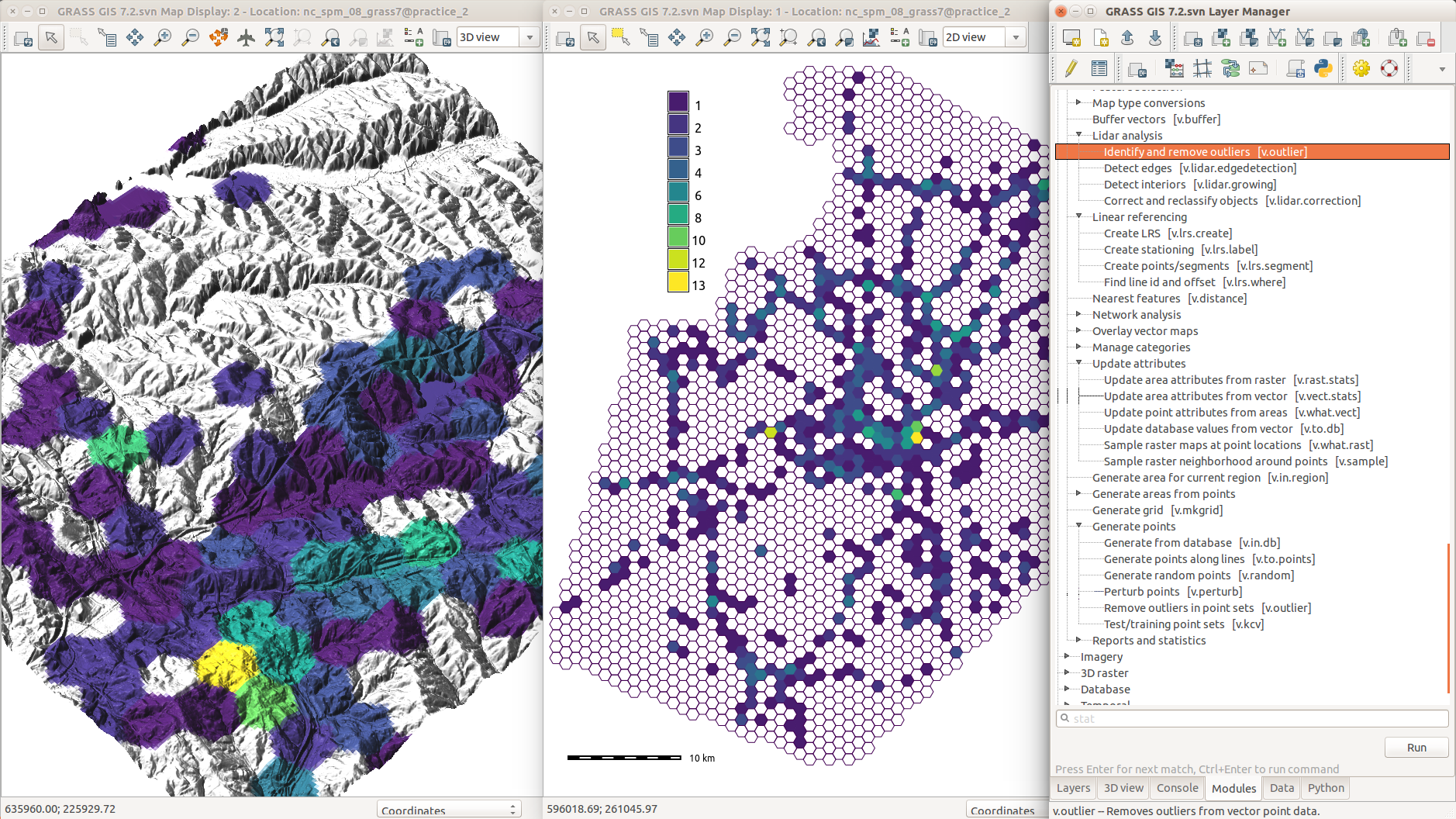
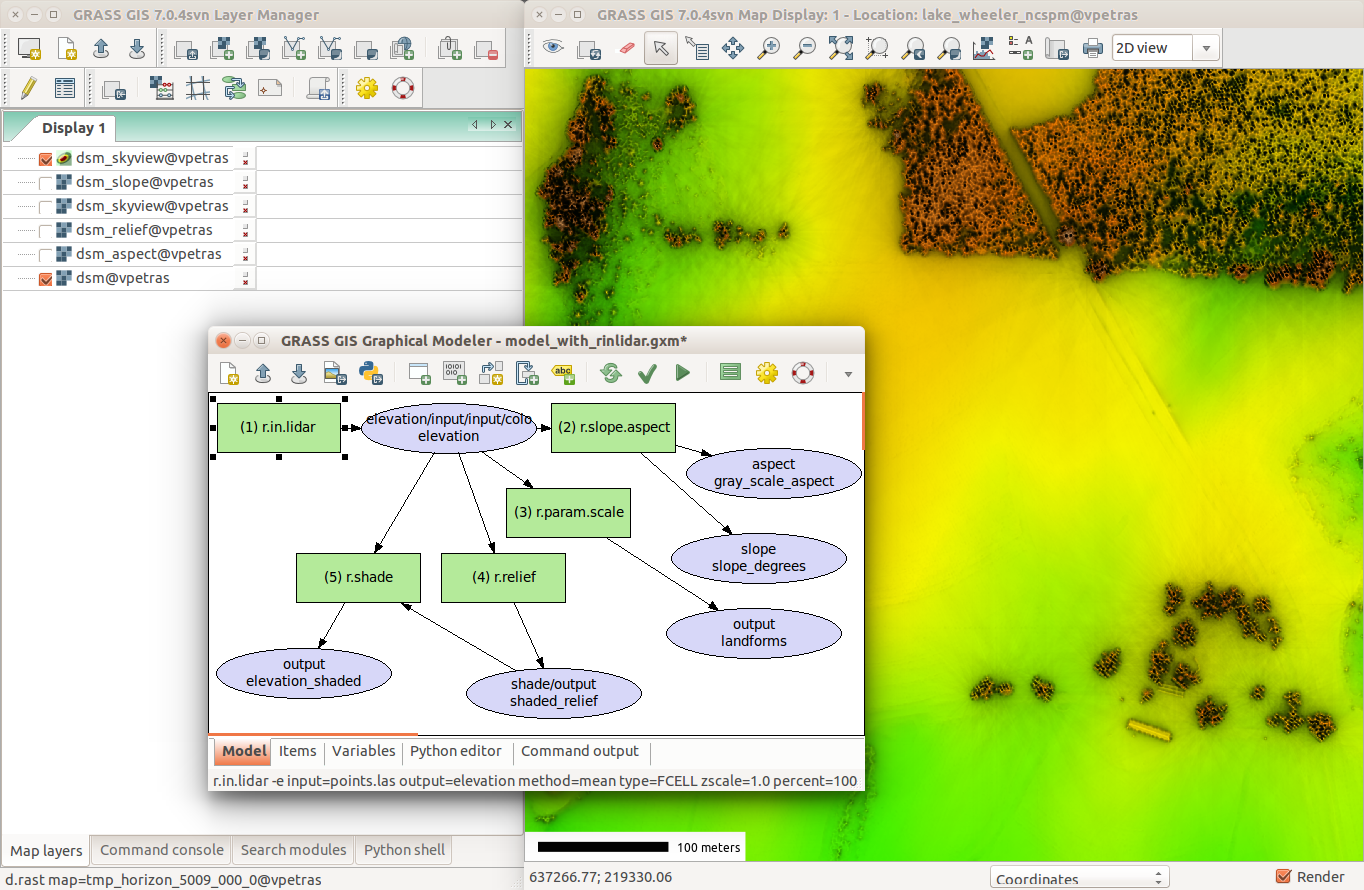
Processing Capabilities
- raster and 3D raster
- map algebra, DEM, interpolation, flow, neighborhood, solar, cost surfaces, ...
- imagery (remote sensing)
- rectification, multispectral, classification, segmentation, PCA, FFT, ML, ...
- vector and database
- buffers, overlays, networks, topology, attribute management, SQL, ...
- spatio-temporal data (time series)
- sampling, statistics, aggregation, temporal topology, algebra, ...
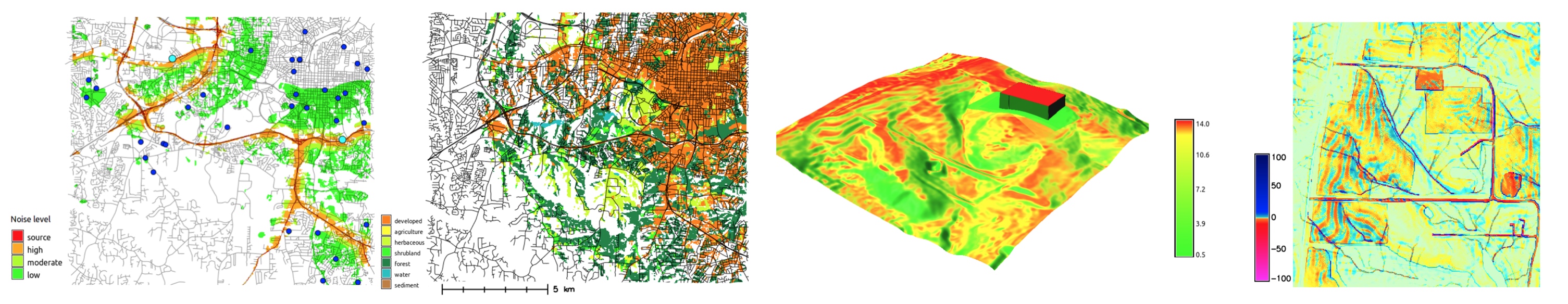
General Capabilities
- visualization
- 2D display, 3D visualization, temporal visualization, PNG, PS and PDF maps, ...
- interoperability
- import from and export to different formats, WMS, ...
- extensibility
- scriptable (e.g. Python), custom tools (typically Python or C), ...
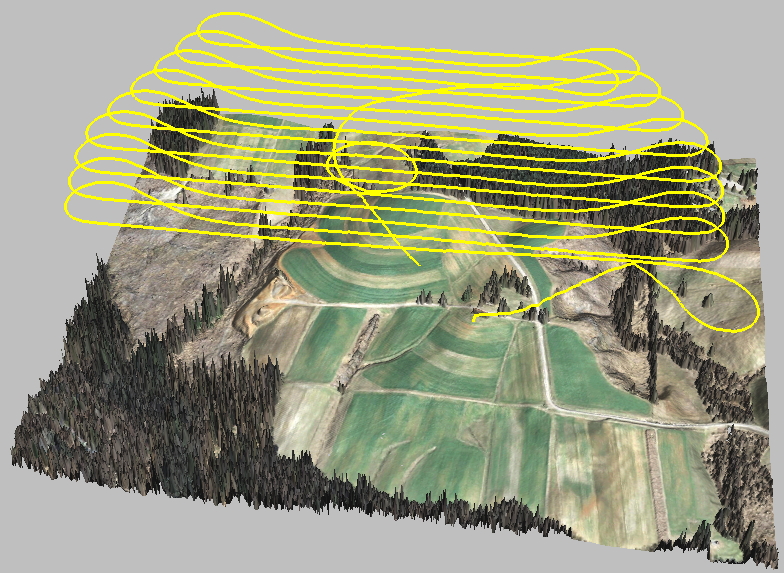
Visualization of a planned drone flight over digital surface model with ortho
Naming Convention for Tools (Modules)
| Prefix | Functionality | Example |
|---|---|---|
| r. | raster processing | r.mapcalc: raster map algebra |
| v. | vector processing | v.surf.rst: interpolation from points to raster |
| g. | general management | g.remove: removes maps |
| d. | display, rendering | d.rast: display raster map |
| i. | imagery processing | i.segment: image segmentation |
| r3. | 3D raster processing | r3.stats: 3D raster statistics |
| t. | temporal data processing | t.rast.aggregate: temporal aggregation |
User Interfaces
Tools (modules) can be accessed using:
- Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Command Line Interface (CLI)
- Python
- Third party interfaces (QGIS, R, ...)
Graphical User Interface
- The interface for a desktop
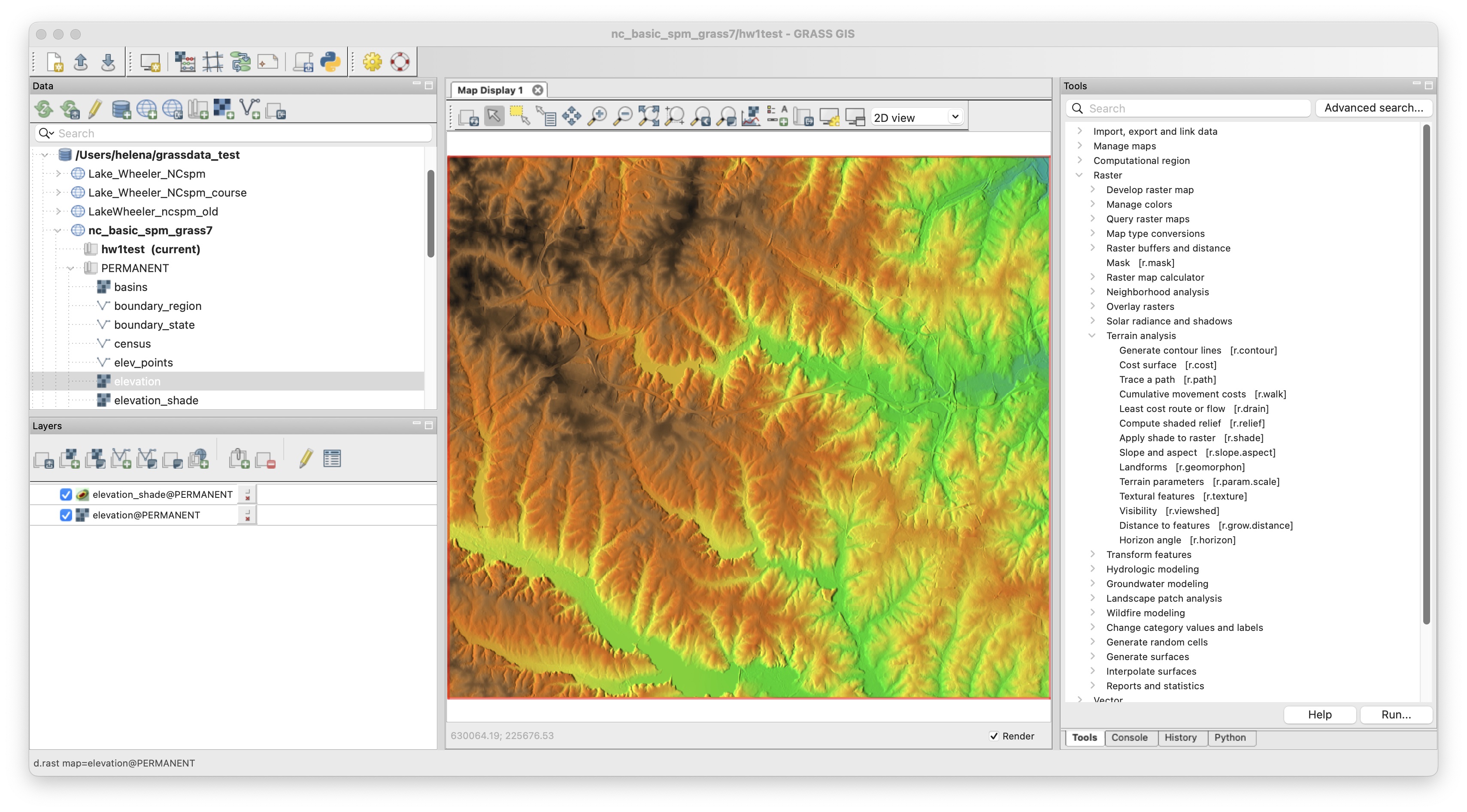
GUI for tools (modules)
- All tools have standardized, unified interface layout.
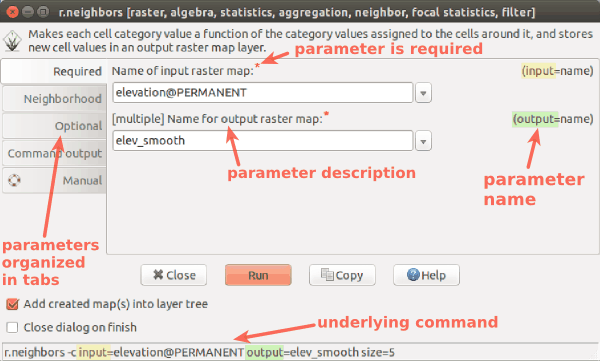
Standard dialog (form) for the r.neighbors tool (module) generates also the command line version
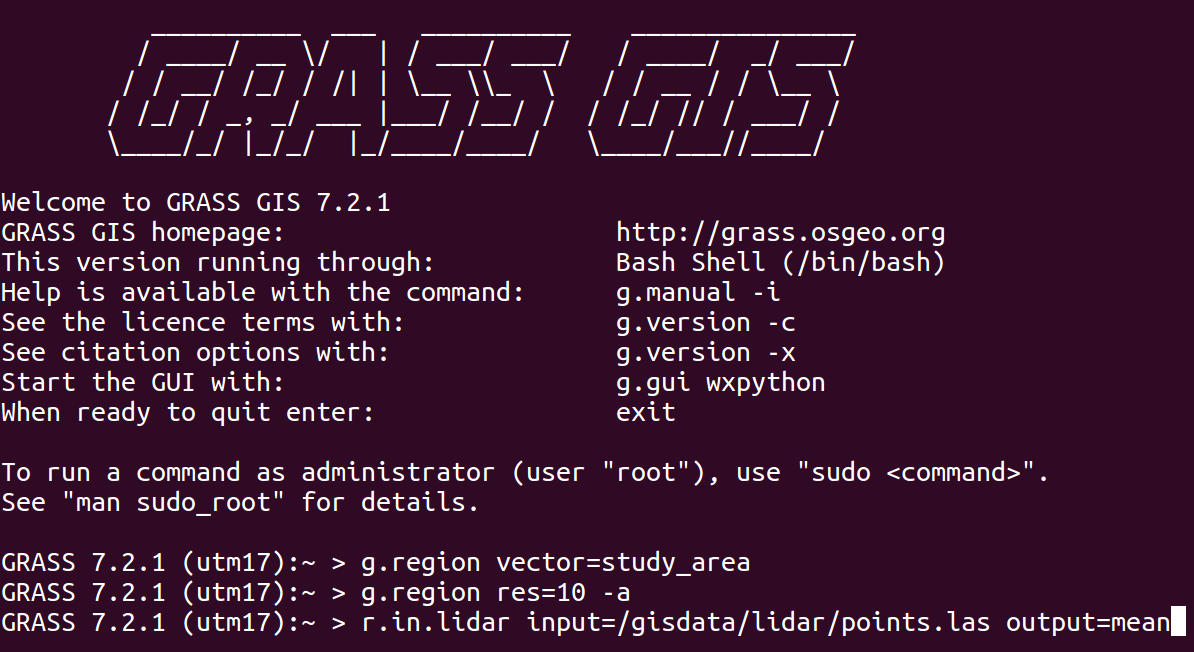
Command Line
- The baseline interface for efficiency and reproducibility
- Available in GUI as Console with autocomplete functions
r.fill.dir input=elev output=fill direction=dir
- and in terminal in Linux or Mac
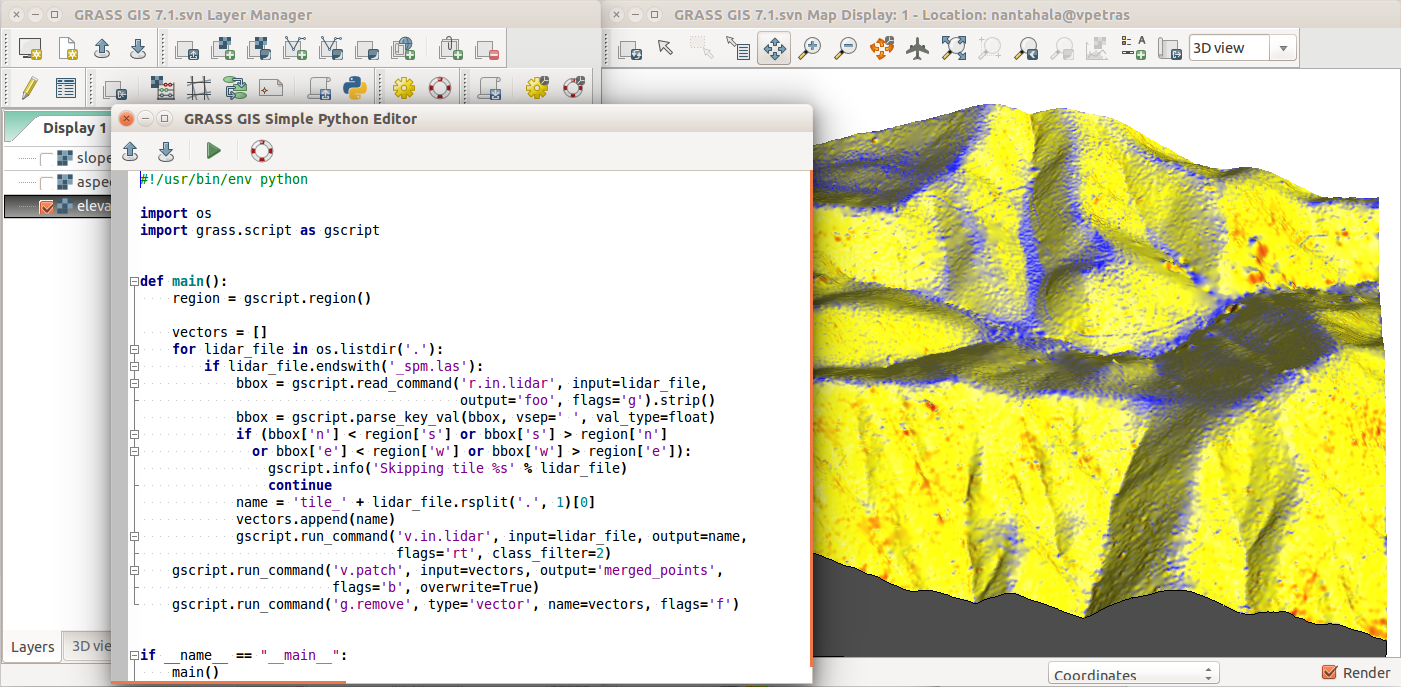
Python
- grass package part of GRASS
- access to tools (modules), but also to internal C functions
- integrated Python editor
- integrates with Jupyter Notebooks
import grass.script as gs
gs.run_command('r.fill.dir', input='elev',
output='fill', direction='dir')
Duality between GUI and commands
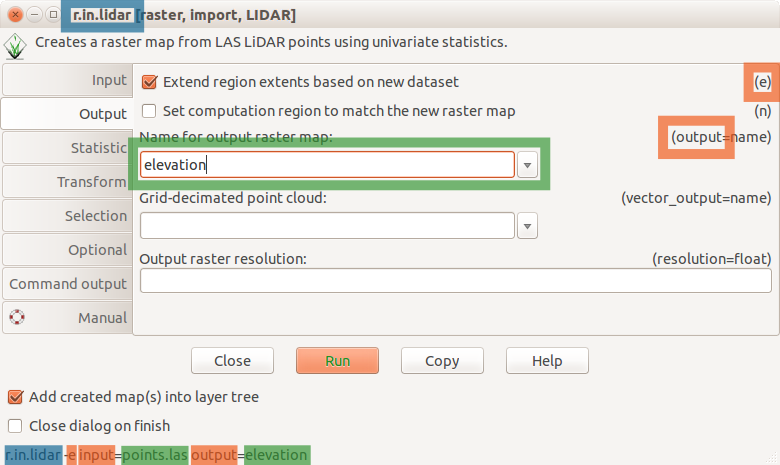
 Python:
Python:

Examples in documentation and class instructions are provided as commands which can be used to fill-in GUI, write Python code, or run directly.
3rd Party Interfaces
- QGIS (Processing Plugin and GRASS Plugin)
- R (rgrass package)
- ...
3rd Party Interfaces
- Tangible Landscape
- tangible user interface to GRASS and Blender
- by NC State University, Center for Geospatial Analytics
Tools running: v.surf.rst, r.contour, r.fill.dir, r.sim.water
see also Petrasova et al., 2018, Tangible Modeling with Open Source GIS, 2nd edition, Springer
Documentation: Users manual
Each tool (module) has a standardized manual page
Public Author & Accessible Code
Manual page includes the author's name(s) and a link to source code
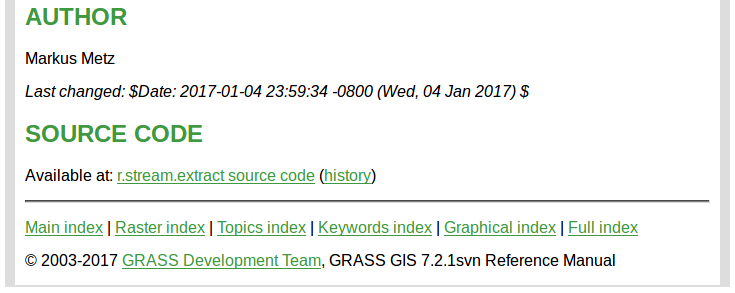
Link to Research Papers
If available, the manual page also includes references to papers describing the methods and algorithms in the tool

Continuing development
- Used as a research platform and code repository
- Example: Solar radiation model
r.sun
- available since 1993
- major changes in 1996, 1999, 2002, 2003, 2006, 2008, 2017
- parallelized version in 7.4
- Hofierka, J., Suri, M. (2002): The solar radiation model for Open source GIS: implementation and applications. International GRASS users conference in Trento, Italy, September 2002.
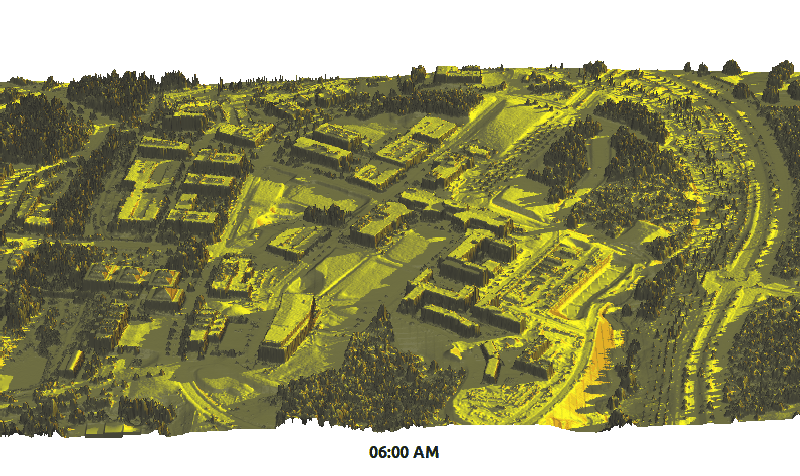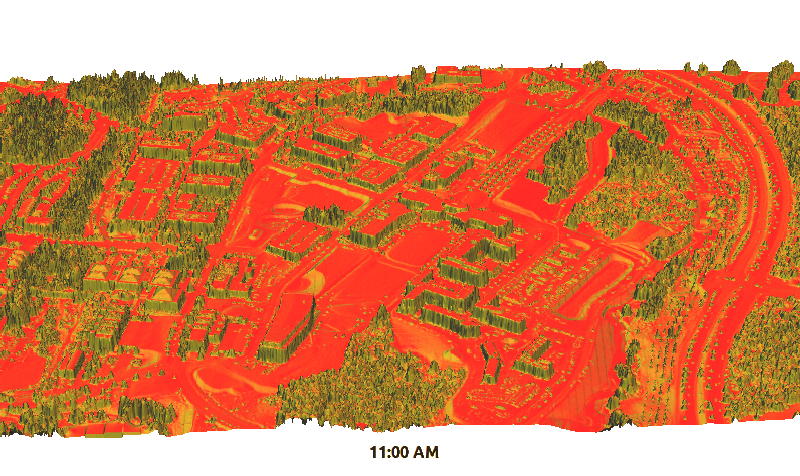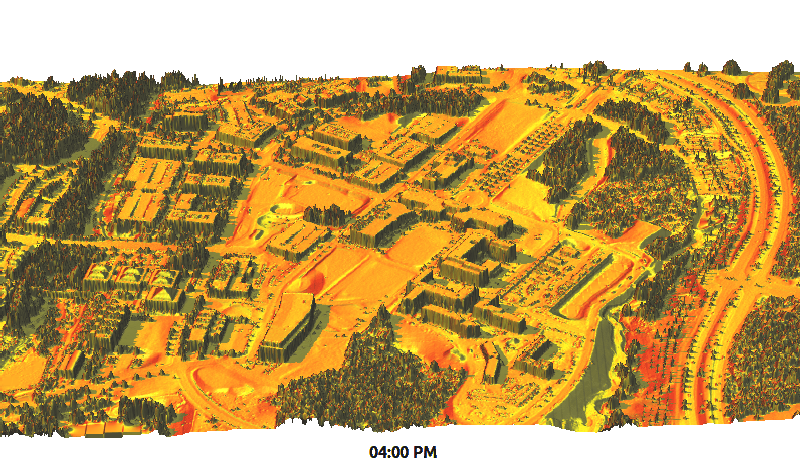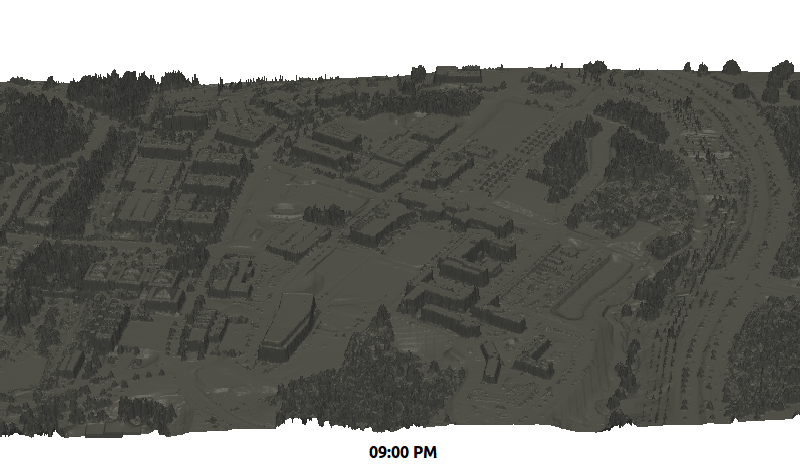
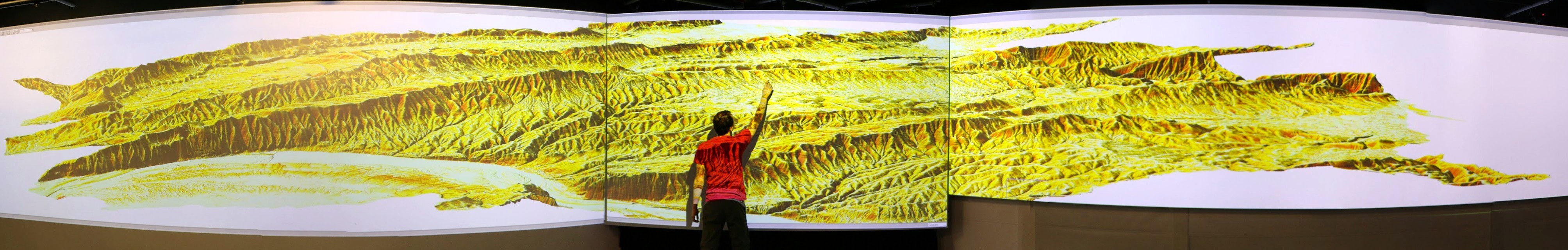
Example application: summer solstice solar radiation dynamics on lidar DEM (Centennial Campus)
Addons Repository
- 300+ user contributed tools
- integrated with g.extension
- including compiled C and C++ for MS Windows
- automatically generated GUI for Python and C/C++
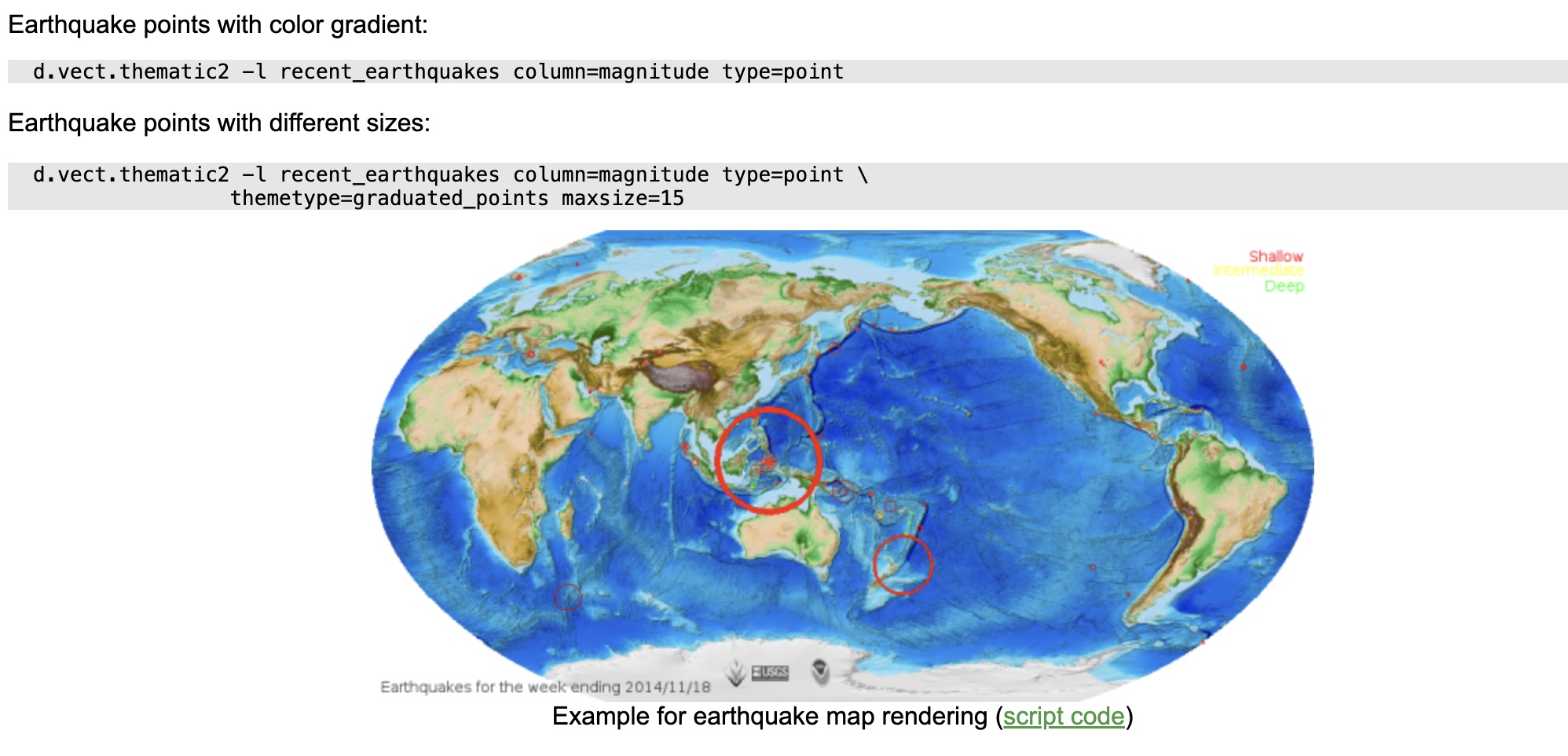 example from d.vect.thematic addon manual page
example from d.vect.thematic addon manual page
Try GRASS with Jupyter Notebooks
GRASS workshops and tutorials implemented as Jupyter Notebooks in Binder:Summary
- General free and open source concepts
- Licensing: No "purchasing of licenses" needed for users
- Brief GRASS overview: example open source geospatial software
- processing capabilities
- several user interfaces
- Class instructions are using GUI and command line
- Python and Jupyter are recommended for the projects
- addon tools
