%% Photogrammetric big-picture workflow
flowchart LR
A["Pre-Processing"] --> B["Data Processing"]
B["Data Processing"] --> C["Data Analysis & Export"]
UAS Imagery Processing
Center for Geospatial Analytics at North Carolina State University
Objectives
- Understand the photogrammetric data processing as a multistep process
- Indicate data needed for orthophoto/DTM generation from aerial imagery
- Understand the difference between interior and exterior orientation of the photo
- Describe the workflow of geoprocessing of aerial imagery
Photogrammetric process

Data processing
Photogrammetric process
%% Photogrammetric big-picture workflow
flowchart LR
subgraph A["Pre-Processing"]
IMAGES["(UAS Images)"]
LOG["(Flight Log / EO)"]
GCP["(GCPs)"]
end
subgraph B["Data Processing"]
MATCH[Feature Matching]
SOLVE["Camera Solving
(SfM / Bundle Adjustment)"]
DENSE[Dense Point Cloud]
MESH[Mesh / Surface]
end
subgraph C["Data Analysis & Export"]
ORTHO[Orthophoto]
DSM[DSM / DTM]
PCLOUD[Classified Point Cloud]
TEXMODEL[Textured 3D Model]
REPORT[Processing Report]
end
IMAGES --> MATCH --> SOLVE --> DENSE --> MESH
SOLVE -. Feedback loop .-> IMAGES
LOG --> SOLVE
GCP --> SOLVE
DENSE --> ORTHO
DENSE --> DSM
DENSE --> PCLOUD
MESH --> TEXMODEL
SOLVE --> REPORT
DENSE --> REPORT
GCP --> REPORT
UAS data
What do we get after the flight mission?
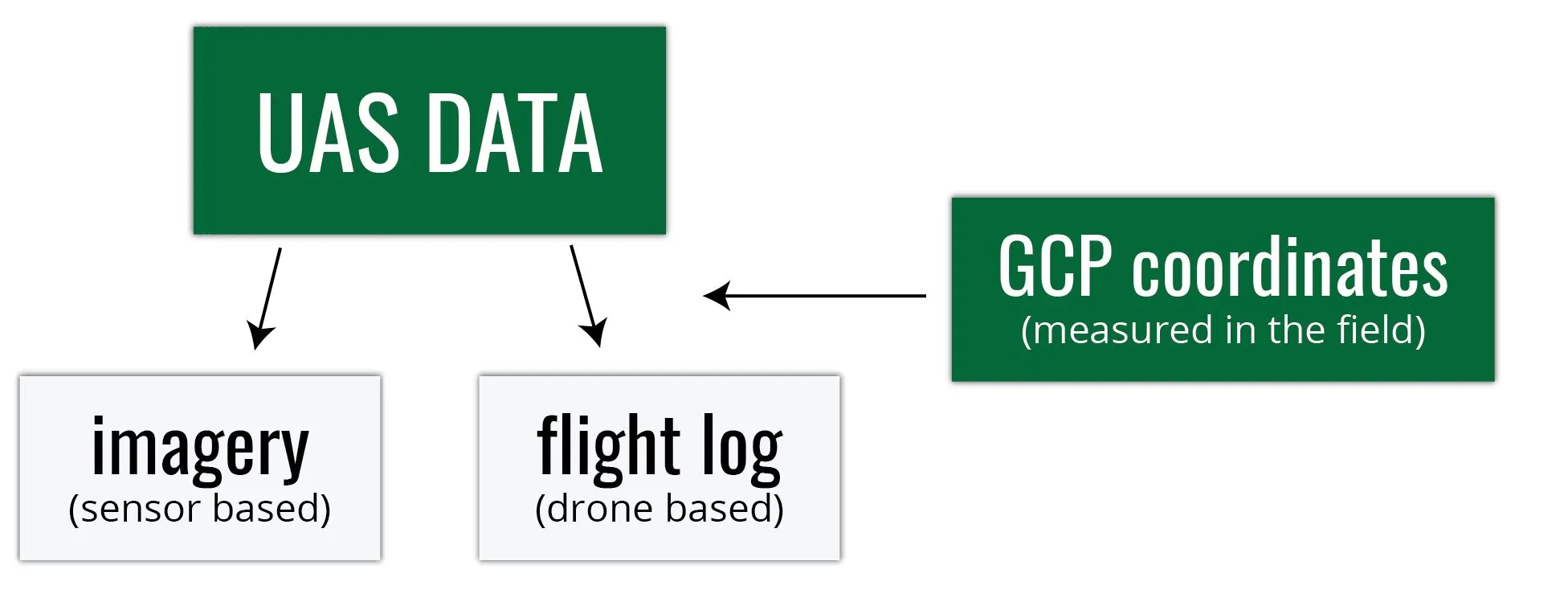
Digital imagery

- usually on the camera SD card
- can be geotagged (depends on camera / UAS setup)
- Camera lens location is “written into” each photo’s EXIF file
- this not always the case..
- Camera lens location is “written into” each photo’s EXIF file
Flight log
- Onboard Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) accurately measures the orientation of airborne sensors,
- Information is logged into a text file (flight log),
- Contains elements of exterior orientation (EO)
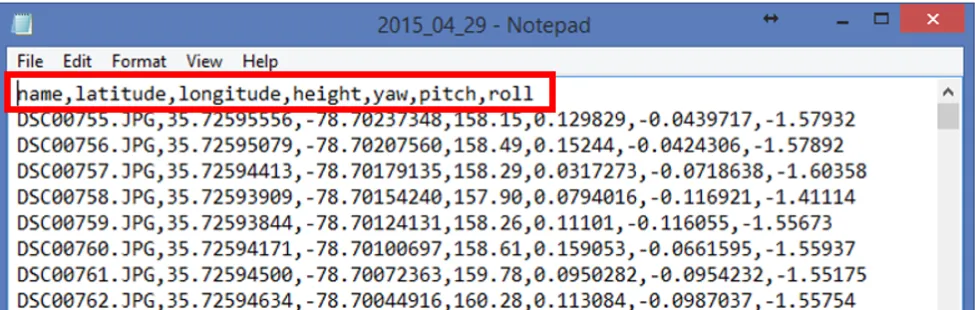
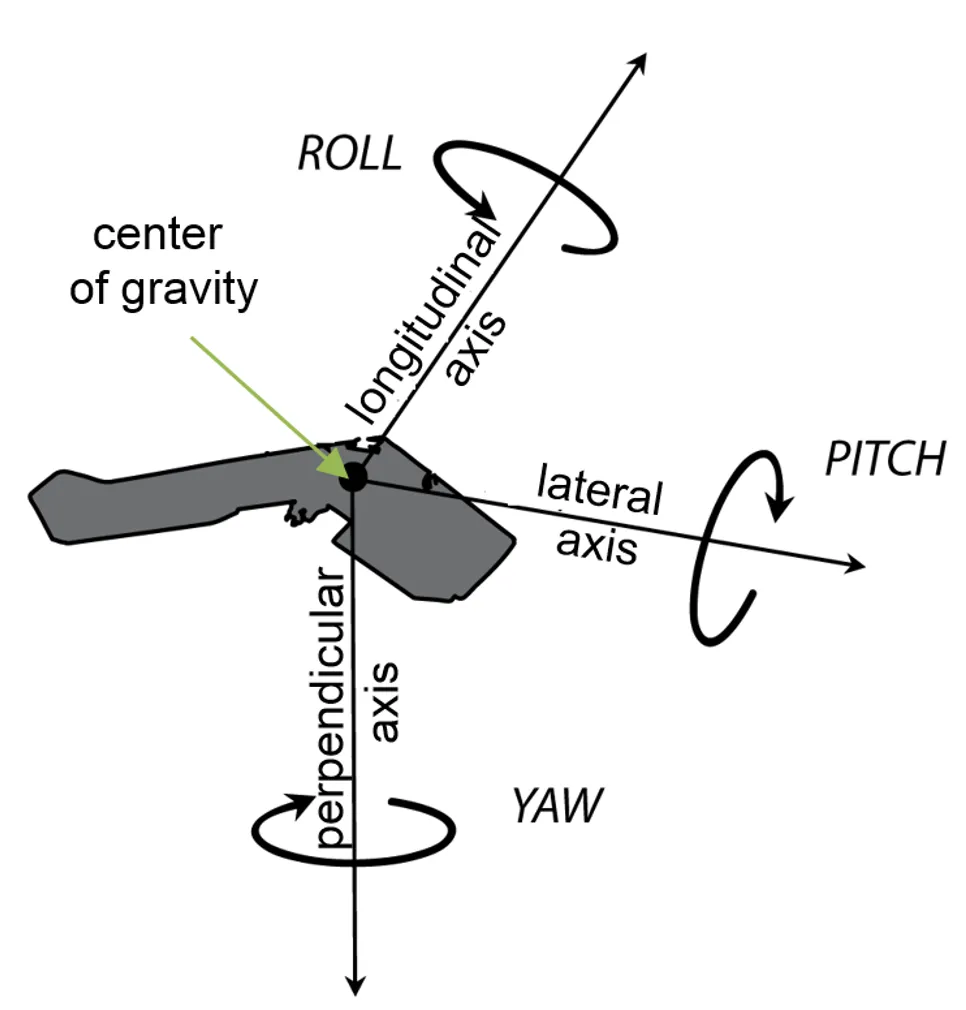
Flight attitude - describes an aircrafts orientation in space (yaw, pitch, roll)
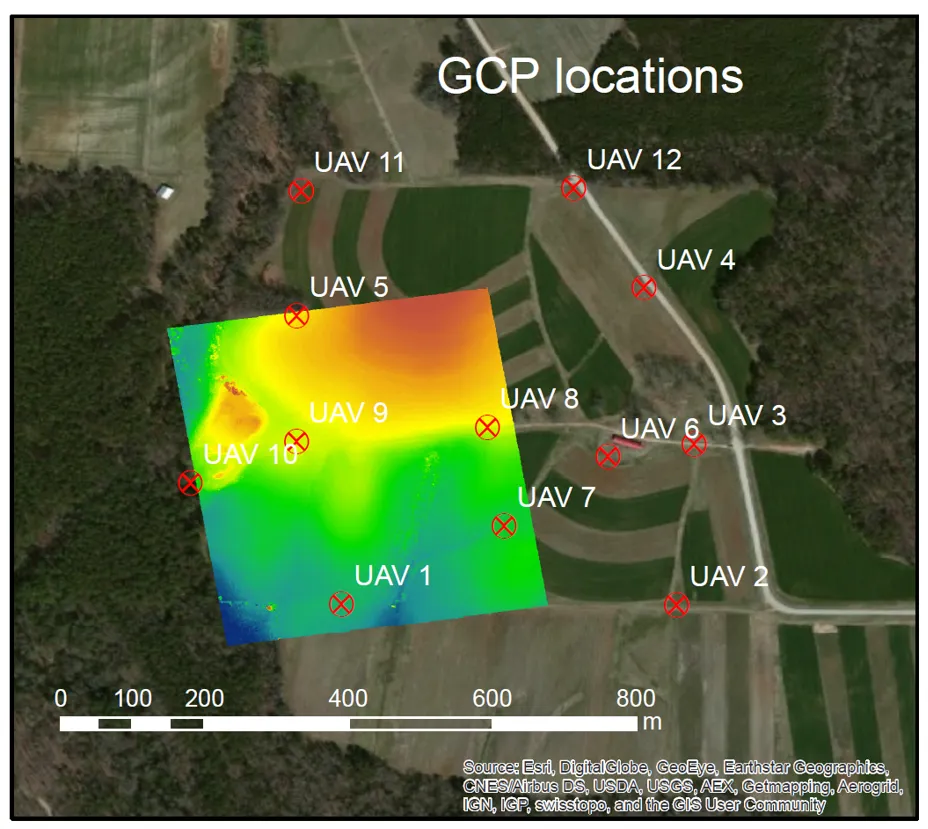
GCP coordinates
- Measured by GPS coordinates of the panels set before the flight
- Photo ID points (distinguishable ground features) can be surveyed later on
- It is important to know the GCPs coordinate system (spatial reference system)
Spatial reference system
- Defines how the two-dimensional, projected map in your GIS is related to real places on the earth
- It is crucial to know what is your data reference system!
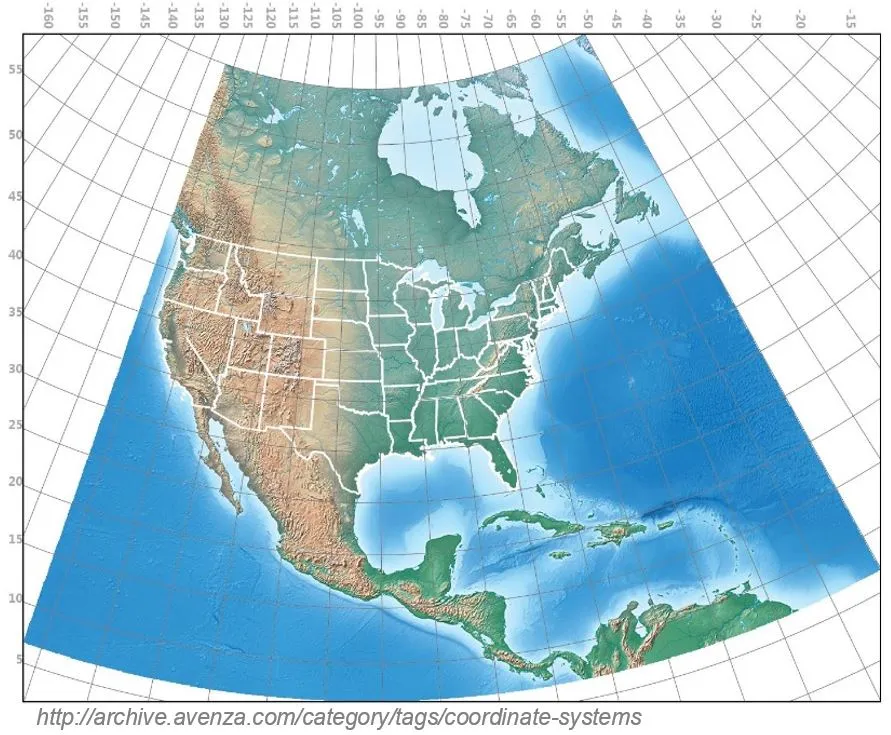
- There are global map projections, but most map projections are created and optimized to project smaller areas of the earth’s surface
- There are two different types of coordinate reference systems: Geographic Coordinate Systems and Projected Coordinate Systems
- Spatial reference list (EPSG codes for coordinate reference systems)
UAS data processing outputs
What do we get after processing the data?
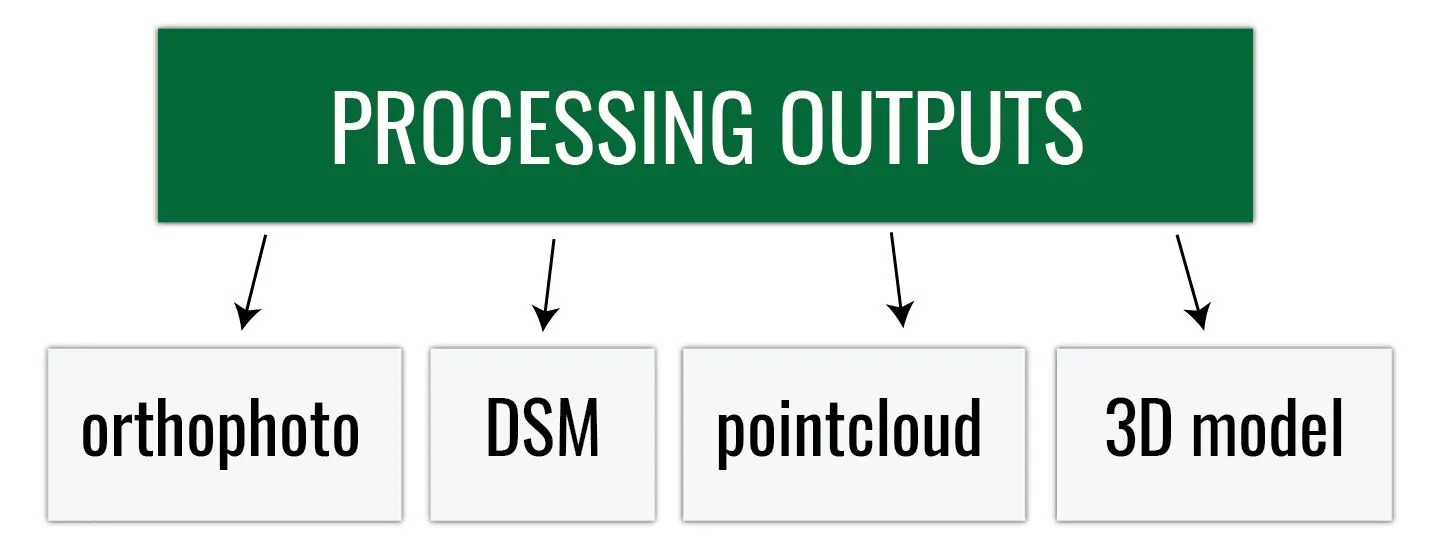
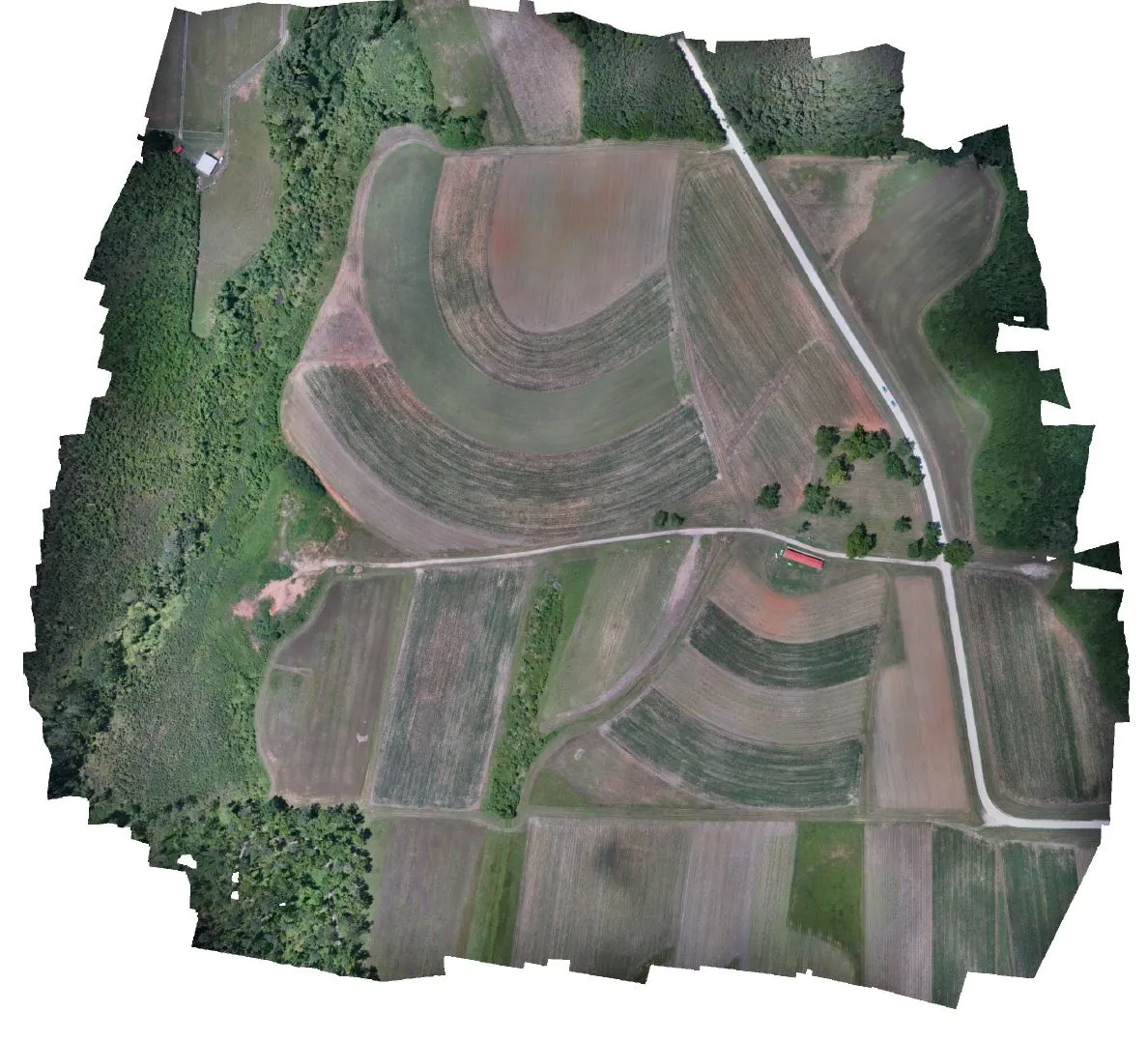
Orthophoto
- Aerial imagery geometrically corrected (“orthorectified”) such that the scale is uniform
- Raster: consists of red, green, and blue bands

Digital Surface Model
- DEM/DTM - Digital Elevation Model / Digital Terrain Model
- Representation of a terrain’s elevation
- Bare-earth raster grid
- DSM - Digital Surface Model
- Representation of a visible surface
- Captures the natural and built features on the Earth’s surface

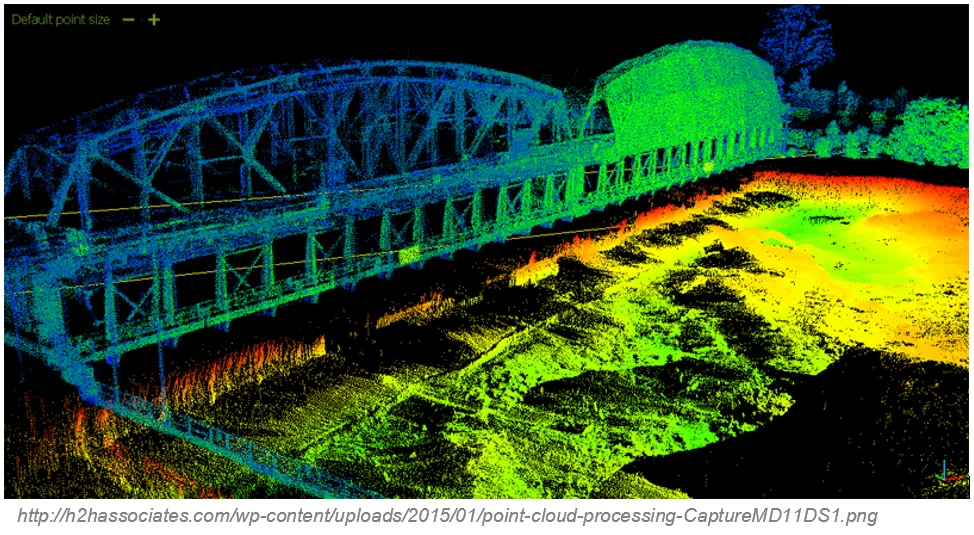
Pointcloud
- Representation of the external surface of an object
- Set of vertices in a three-dimensional coordinate system
- Vector or raster?
- Dale Lutz once said, “point cloud is a badly behaved raster”

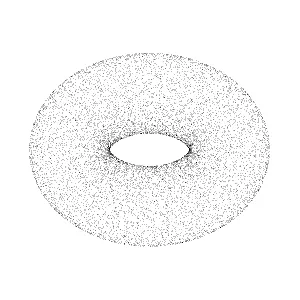
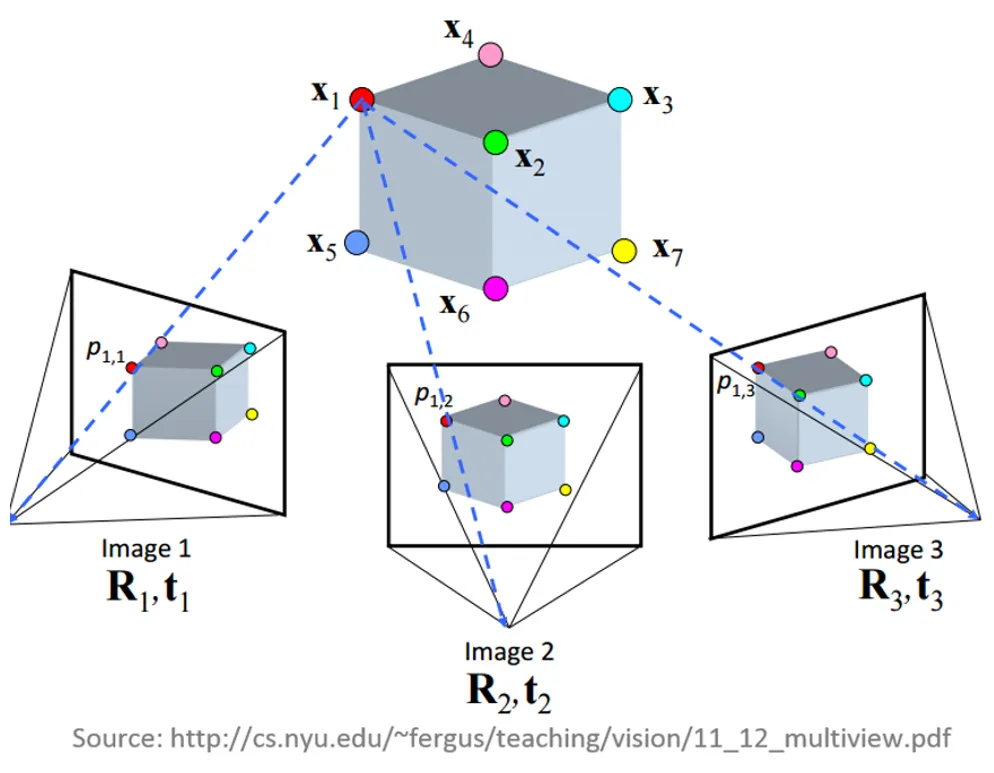
Multiple-view geometry
- Scene geometry (structure):
Given 2D point matches in two or more images, where are the corresponding points in 3D? - Correspondence (stereo matching):
Given a point in just one image, how does it constrain the position of the corresponding point in another image? - Camera geometry (motion):
Given a set of corresponding points in two or more images, what are the camera matrices for these views?
What do we need?
- Digital imagery
- (Digital elevation model or topographic dataset)
- Exterior orientation parameters from aerial triangulation or IMU
- Optional(Camera calibration report)
- Optional(Ground Control Points parameters)
- Photogrammetric processing software that utilizes collinearity equations
Digital imagery


Digital Elevation Model
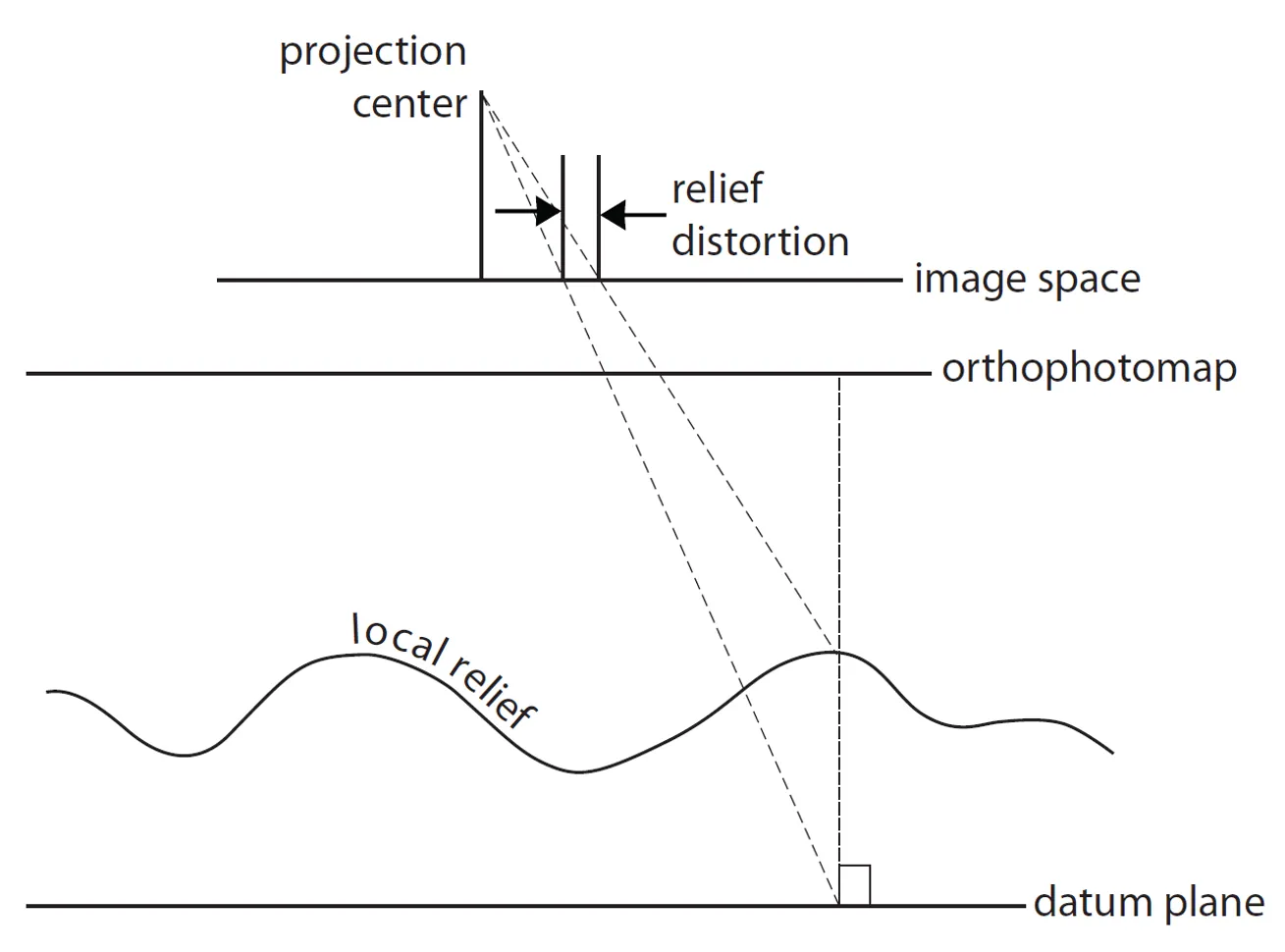
In the past: Shape of the ground surface must be known in order to remove the effects of relief displacement
Now: Computed automatically by Structure from Motion
Structure from Motion (SfM)
- Range imaging technique
- Process of estimating 3D structures from 2D image sequences
- May be coupled with local motion signals
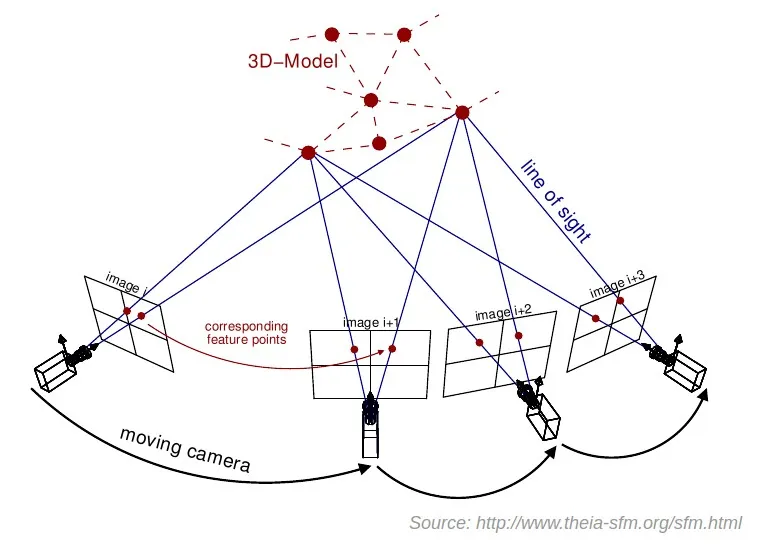
Exterior orientation (EO)
Position and orientation in the object space
6 elements necessary for any photogrammetric processing:
The cameras:
- X (Latitude)
- Y (Longitude)
- Z (Altitude)
and Angular orientation:
| Photogrammetry | Aviation analogy | Axis | Motion |
|---|---|---|---|
| ω (omega) | Roll | x | Tilt forward/back |
| φ (phi) | Pitch | y | Tilt side-to-side |
| κ (kappa) | Yaw | z | Rotation around vertical |
Flight log (Again)
- Log file contains elements of exterior orientation that are measured by onboard Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) and written into a text file

- Sometimes (most DJI products) exterior orientation parameters are saved in photos’ EXIF file
- Log contains information about the location of the camera, not the location of the depicted object - more info in this section of lecture 3
Interior orientation
- In the past: camera calibration report
- Now: Self-calibration (auto-calibration) is the process of determining intrinsic camera parameters directly from uncalibrated images
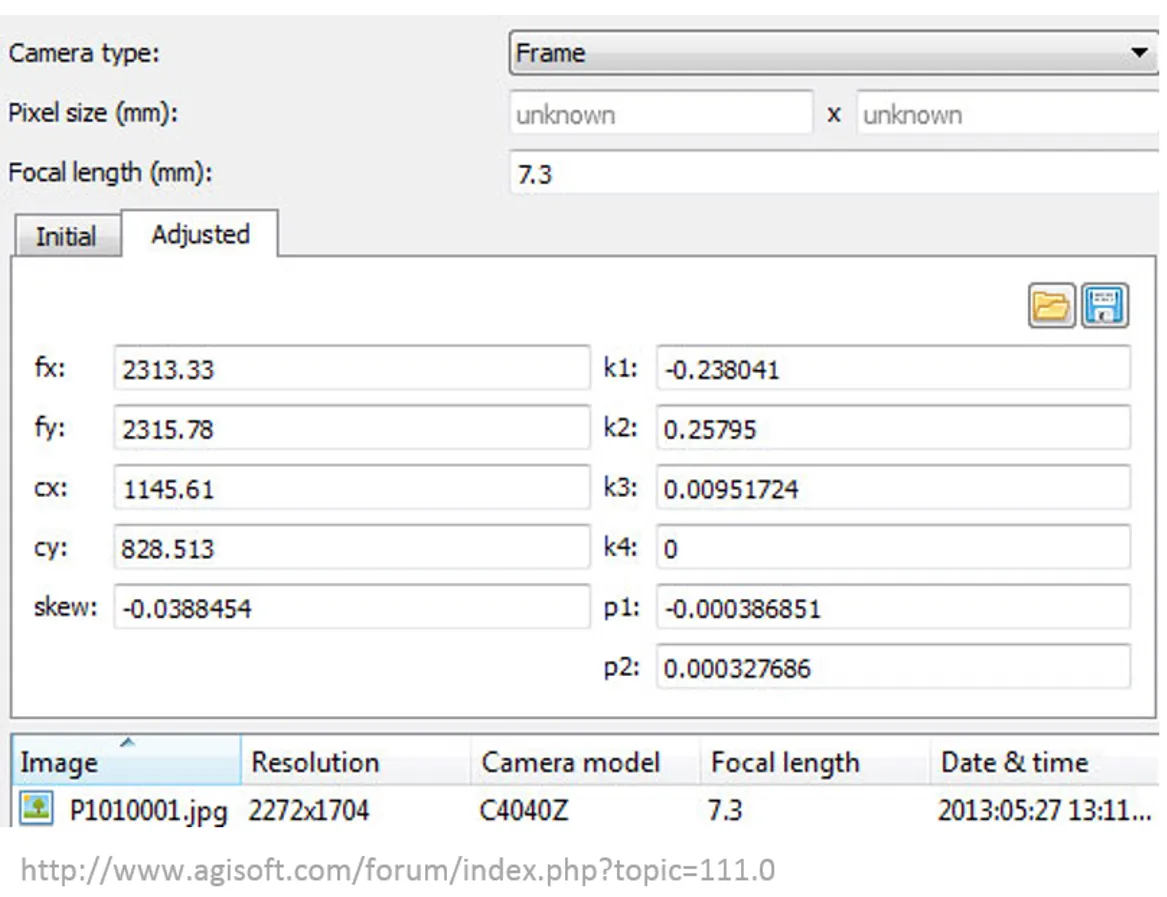
- Can be automatically derived using Structure from Motion (SfM) methods
Ground Control Points
- GCP - Target in the project area with known 3 coordinates (X, Y, Z or lat, long, alt)
- For more information about placing targets and importance of GCPs see this section of lecture 3
- For more information about processing the data with GCPs see intro to the assignment

Processing options
Everything boils down to… money (and time)
- What is my starting budget and equipment?
- How frequently will I fly?
- Do I have the experience/training necessary for processing (or am I able to hire people who do)?
- Do I have time to process the data by myself?
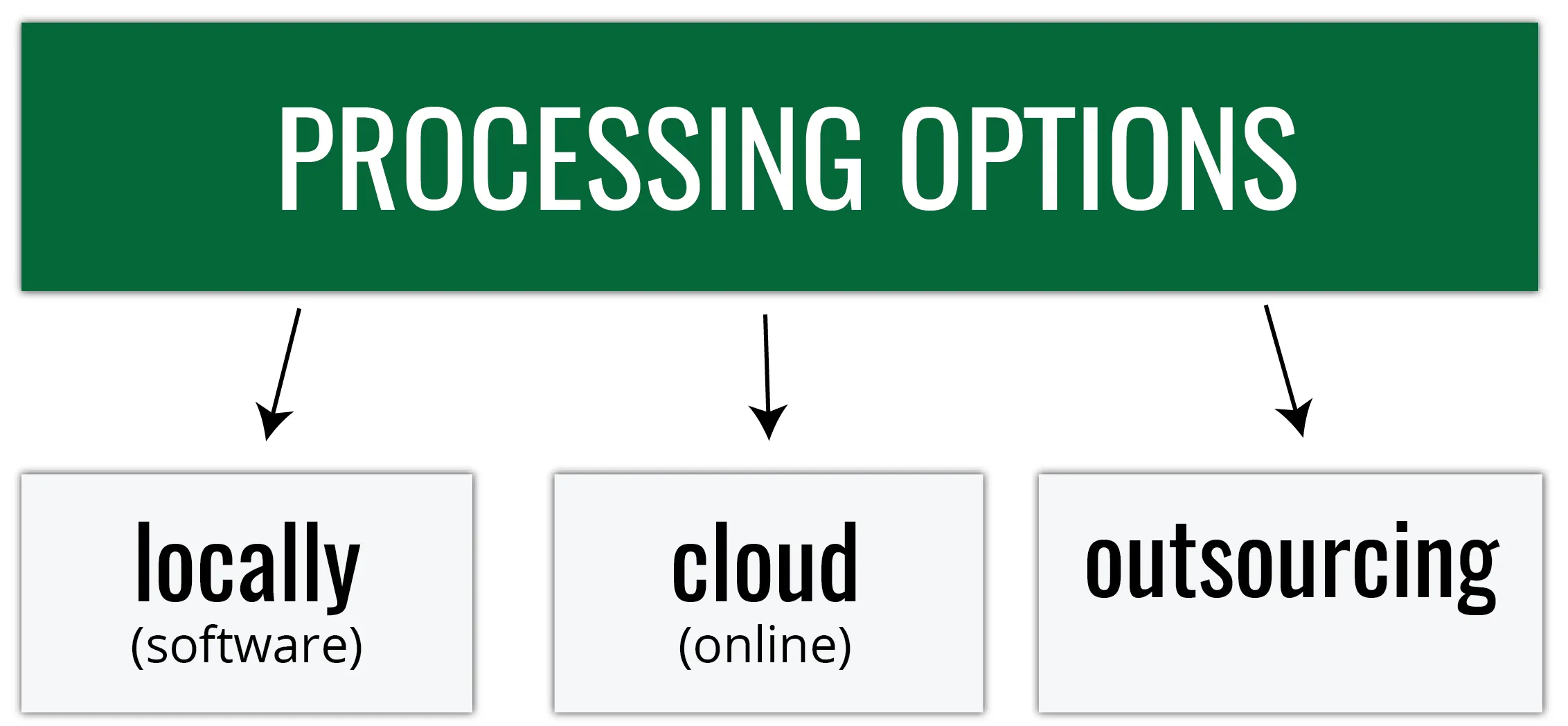
Processing options - software
Agisoft Metashape
- Image-based solution aimed at creating 3D content from still images
- Operates with arbitrary images and is efficient in both controlled and uncontrolled conditions
- Both image alignment and 3D model reconstruction are fully automated
Processing workflow
Preprocessing stage:

- Loading photos into Metashape
- Inspecting loaded images, removing unnecessary images
Processing workflow
Processing stage:

- Aligning photos
- Building dense point cloud
- (optional: editing dense point cloud)
- Building mesh (3D polygonal model)
- (optional: editing mesh)
- Generating texture
- Building DSM and orthomosaic
Exporting results


Preprocessing
- Loading photos
- Loading camera positions (flight log)
- If the EO is in the photos EXIF file, the parameters will load automatically

Aligning photos
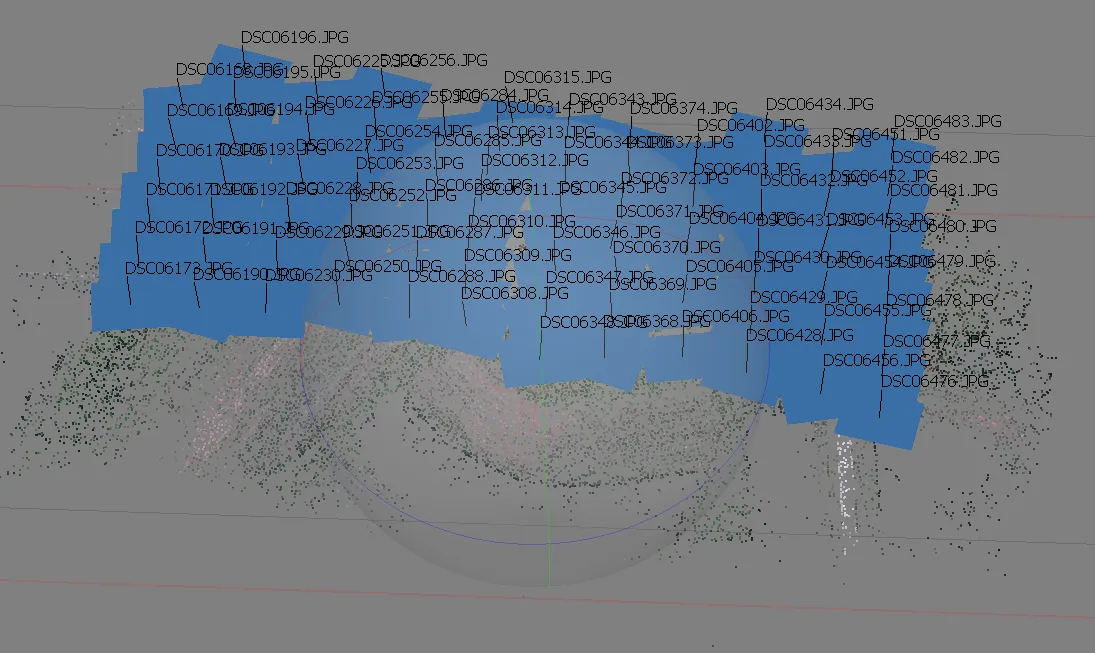
At this stage, Agisoft Metashape implements SfM algorithms to monitor the movement of features through a sequence of multiple images:
- Obtains the relative location of the acquisition positions
- Refines camera calibration parameters
- Sparse point cloud and a set of camera positions are formed

Bundle Block Adjustment
- Non-linear method for refining structure and motion
- Minimizing reprojection error
- Detecting image feature points (i.e., various geometrical similarities such as object edges or other specific details)
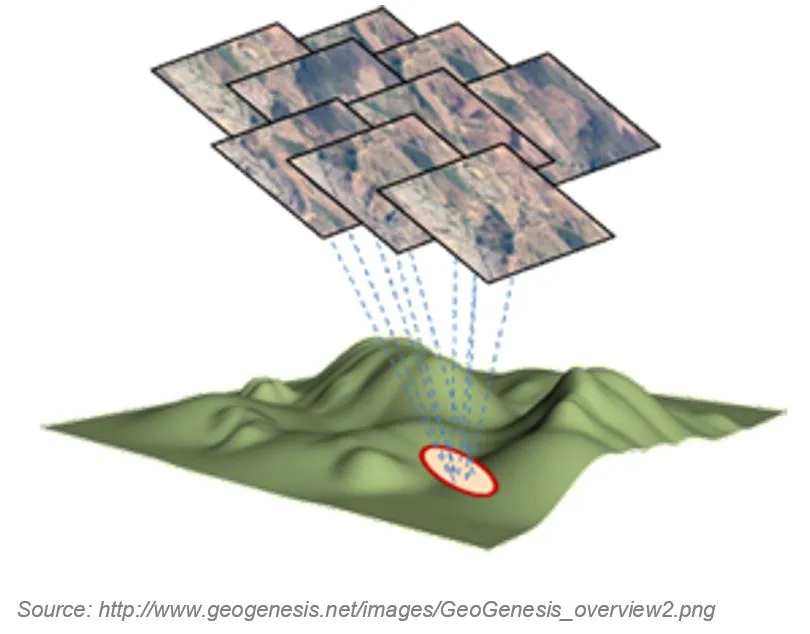
Bundle Block Adjustment
- Subsequently monitoring the movement of those points throughout the sequence of multiple images
- Using this information as input, the locations of those feature points can be estimated and rendered as a sparse 3D point cloud
Aligning cameras in Metashape
Accuracy
- Higher accuracy > more accurate camera position estimates (time-consuming)
- Lower accuracy > rough camera positions (less-time consuming)
Works by upscaling or downscaling images when identifying tie points.
Building dense point cloud (Depth Maps)
At the stage of dense point cloud generation, Agisoft calculates depth maps for every image
- Quality: Highest, High, Medium, Low, Lower > the higher quality, the more accurate camera position estimates, but the process is more time-consuming
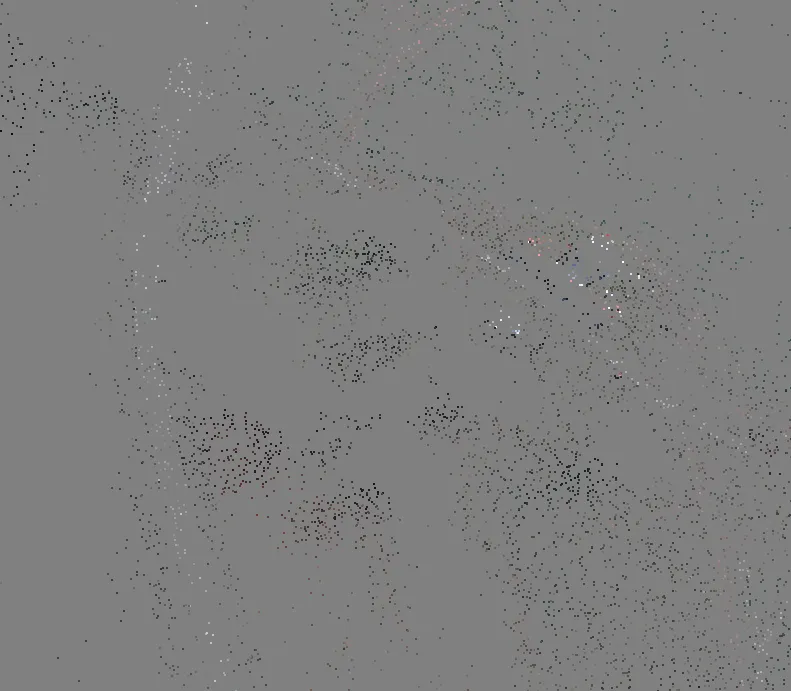


Building dense point cloud (Depth Filtering Modes)
Depth Filtering modes
Algorithms sorting outliers (due to some factors, like poor texture of some elements of the scene, noisy or badly focused images)
- Mild depth filtering mode > for complex geometry (numerous small details on the foreground), for important features not to be sorted out
- Moderate depth filtering mode > results in between the Mild and Aggressive
- Aggressive depth filtering mode > sorting out most of the outliers (Recommended for aerial data processing)
Optional: Editing dense point cloud
- Manual points removal
- Automatic filtering based on applied masks
- Sparse cloud only:
- Reducing the number of points in the cloud by setting tie point per photo limit
- Automatic filtering based on:
- Reprojection error
- Reconstruction uncertainty
- Image count
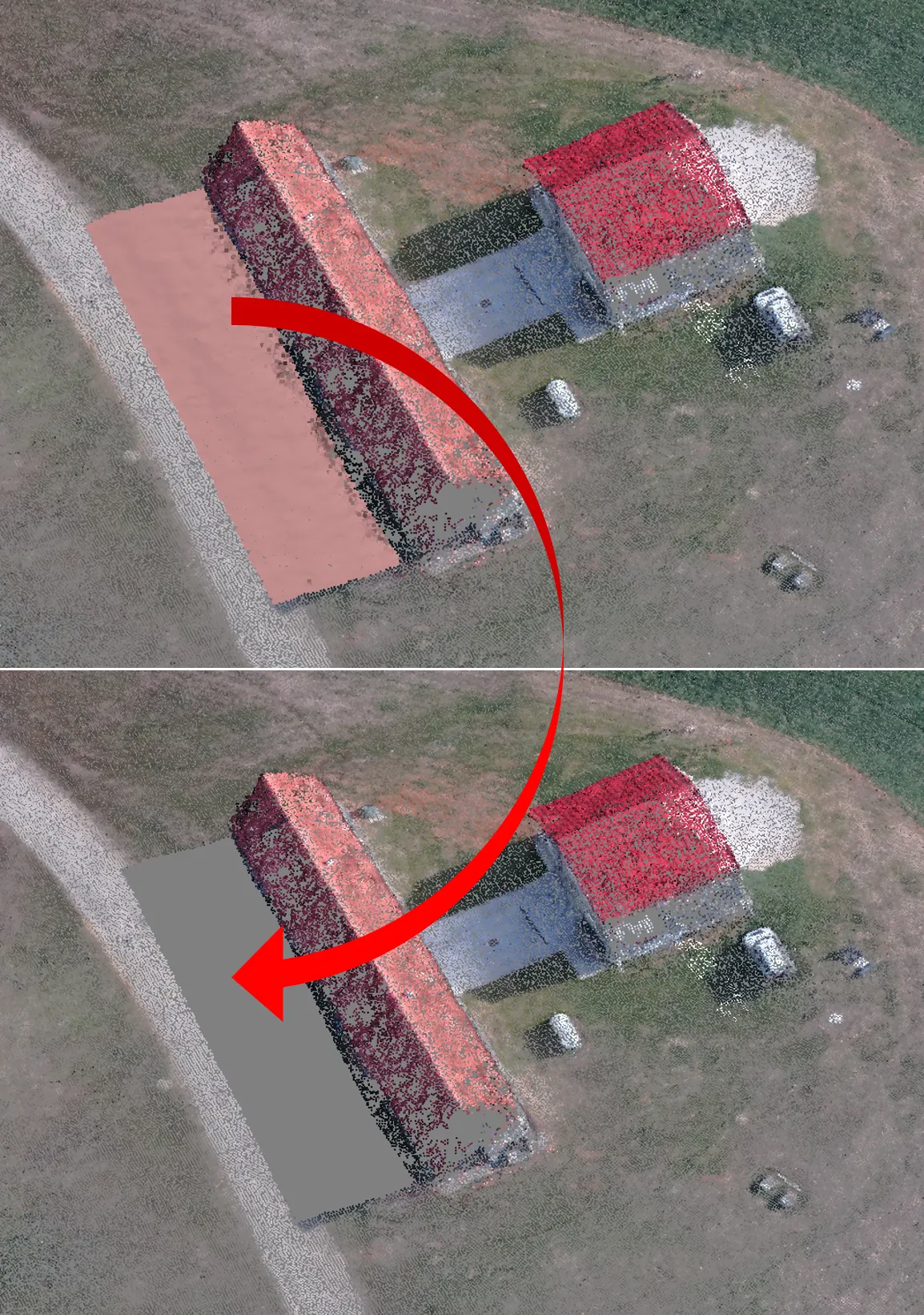

Building mesh
- Arbitrary > for modeling of any kind of object
- Should be selected for closed objects (statues, buildings, etc.)
- Memory consumption: high
- High field > for modeling of planar surfaces
- Should be selected for aerial photography
- Memory consumption: low
- Allows for larger data sets processing
- Source data > the source for the mesh generation
- Sparse cloud > fast 3D model generation (low quality)
- Dense cloud > high-quality output based on the previously reconstructed dense point cloud
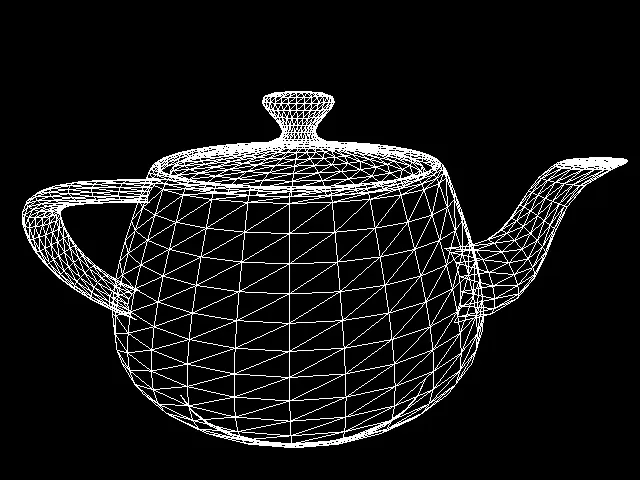

Building mesh (Face Count)
Face count > the maximum face count in the final mesh
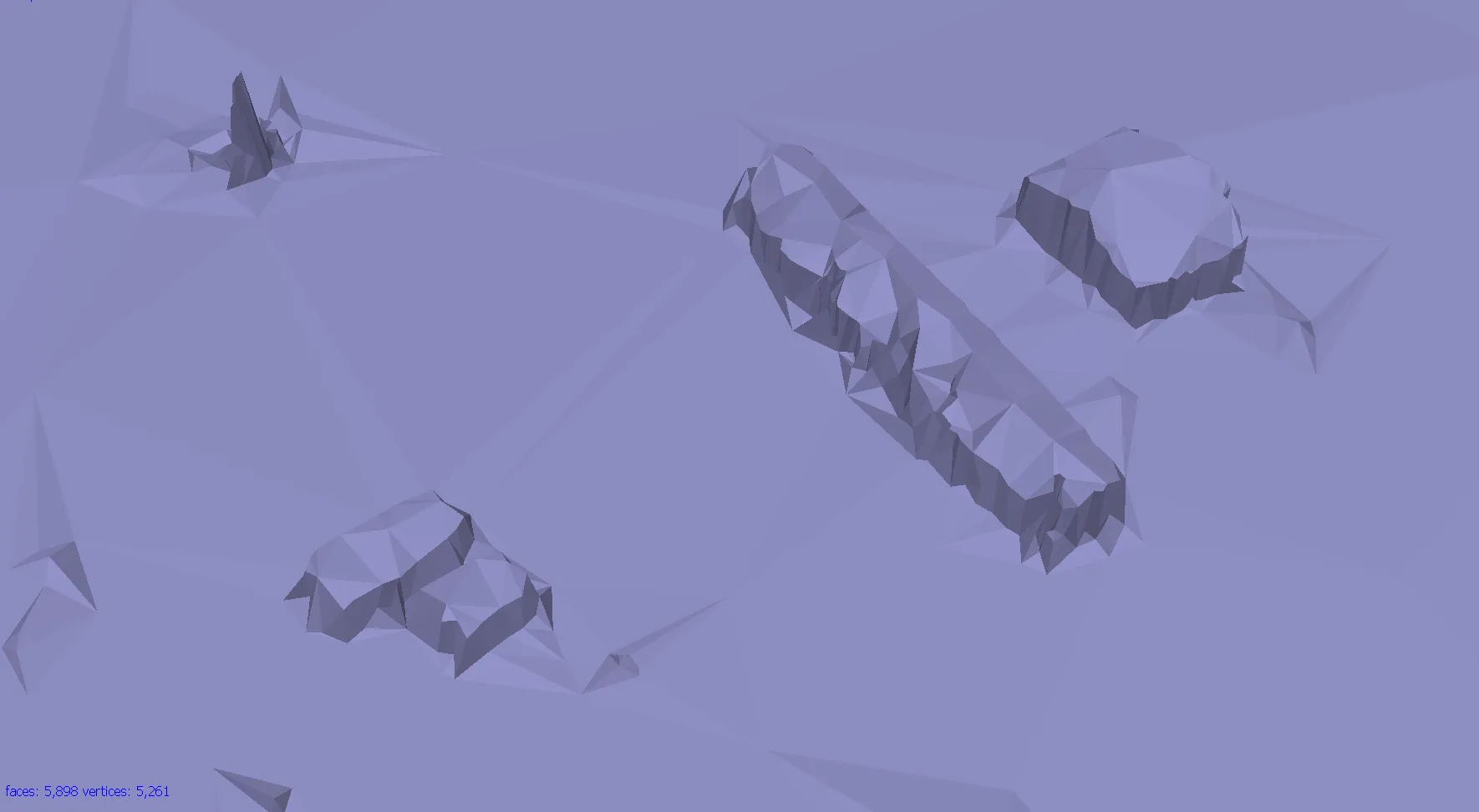

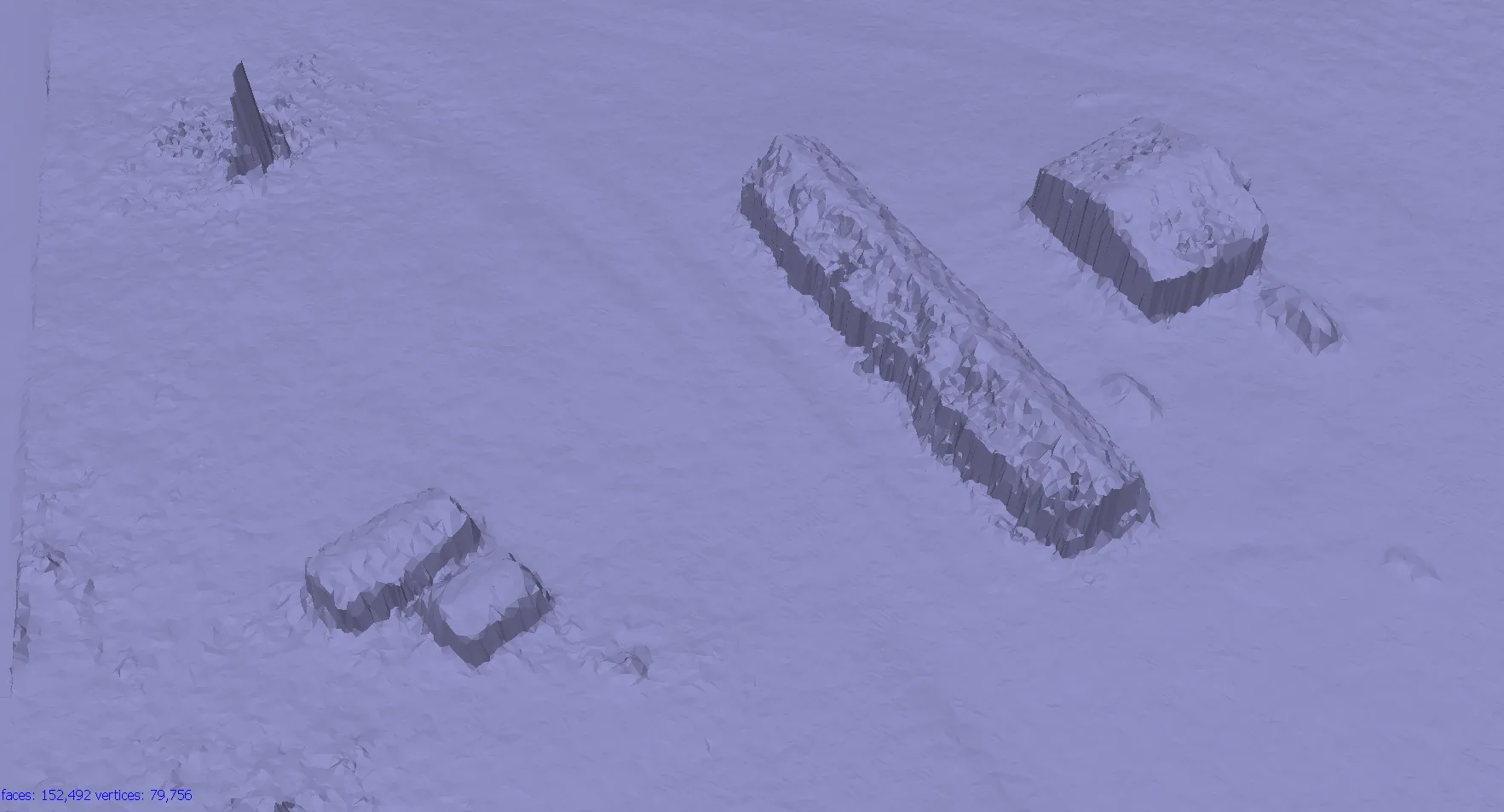
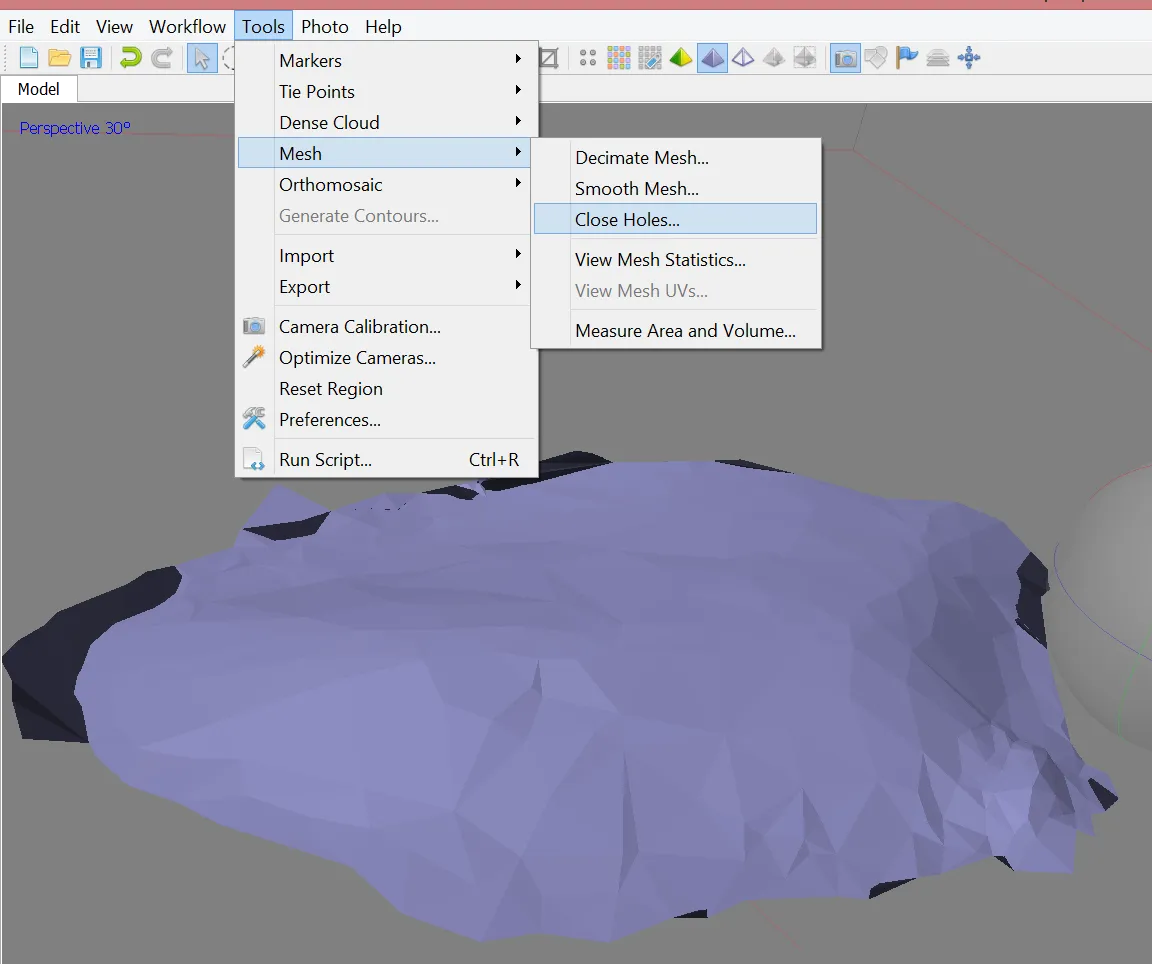
Optional: Editing mesh
- Close Holes tool > repairs your model if the reconstruction procedure resulted in a mesh with several holes, due to insufficient image overlap
- Necessary step for volumes calculation
- Decimation tool > decreases the geometric resolution of the model by replacing a high-resolution mesh with a lower resolution one
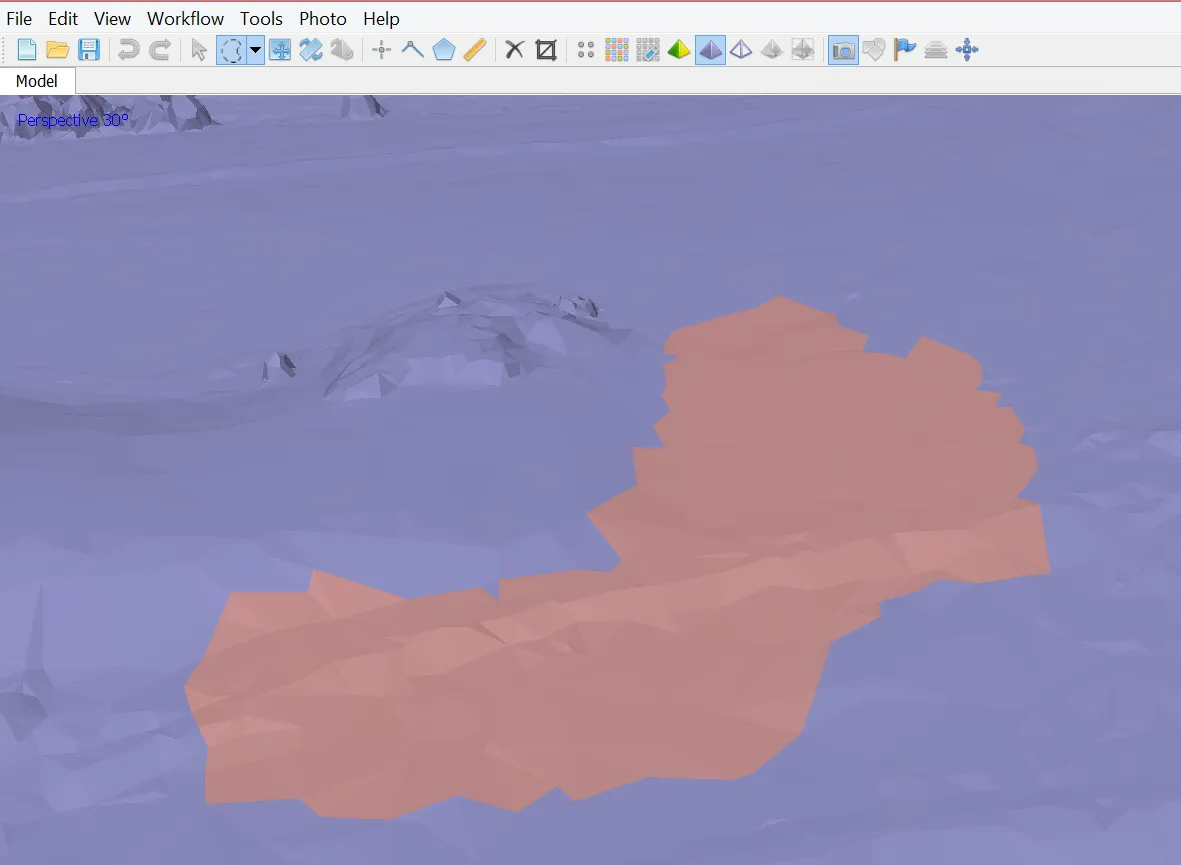
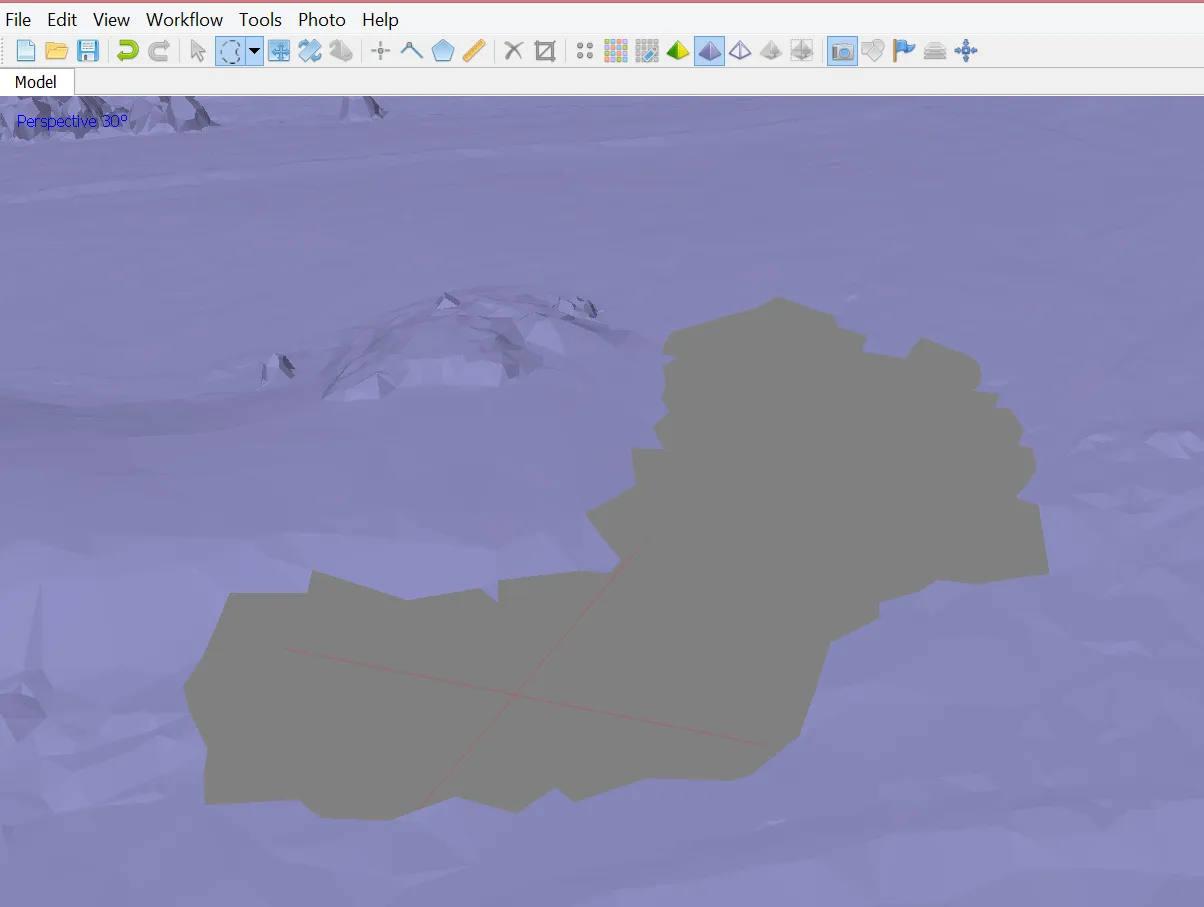
Optional: Editing mesh
- Automatic filtering based on specified criteria:
- Connected component size
- Polygon size
- Manual polygon removal
- Fixing mesh topology
- Editing mesh in the external program
- Export mesh for editing in the external program
- Import edited mesh
Generating texture
- Determines how the object texture will be packed in the texture atlas
- Affects the quality of the final model
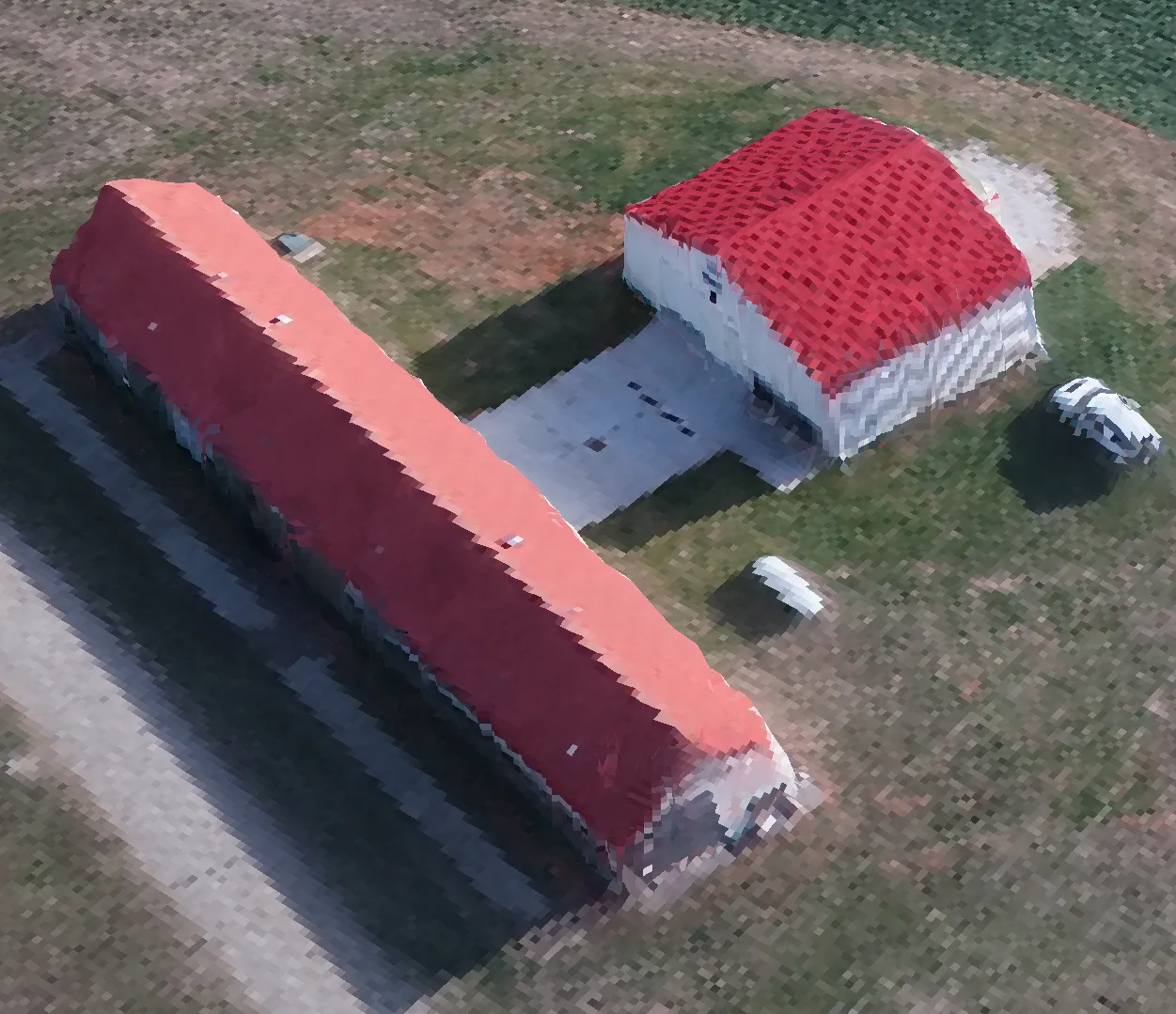

- Texture mapping modes:
- Generic
- Adaptive orthophoto
- Orthophoto
- Spherical
- Single photo
- Keep uv
Texture mapping modes
Generic
- Creates as uniform texture as possible
Adaptive orthophoto
- The object surface split into the flat part and vertical regions
- The flat part of the surface textured using the orthographic projection, while vertical regions textured separately to maintain accurate texture representation in such regions
- More compact texture representation for nearly planar scenes + good texture quality for vertical surfaces
Texture mapping modes
Orthophoto
- The whole object surface textured in the orthographic projection
- Even more compact texture representation than the Adaptive orthophoto at the expense of texture quality in vertical regions
Spherical
- Only for objects that have a ball-like form
Single photo
- Texture from a single photo (photo can be selected from ‘Texture from’ list)
Keep uv
- Generates texture atlas using current texture parametrization; Rebuilding current texture with different resolution or generating the atlas parametrized in the external software
Generating DSM
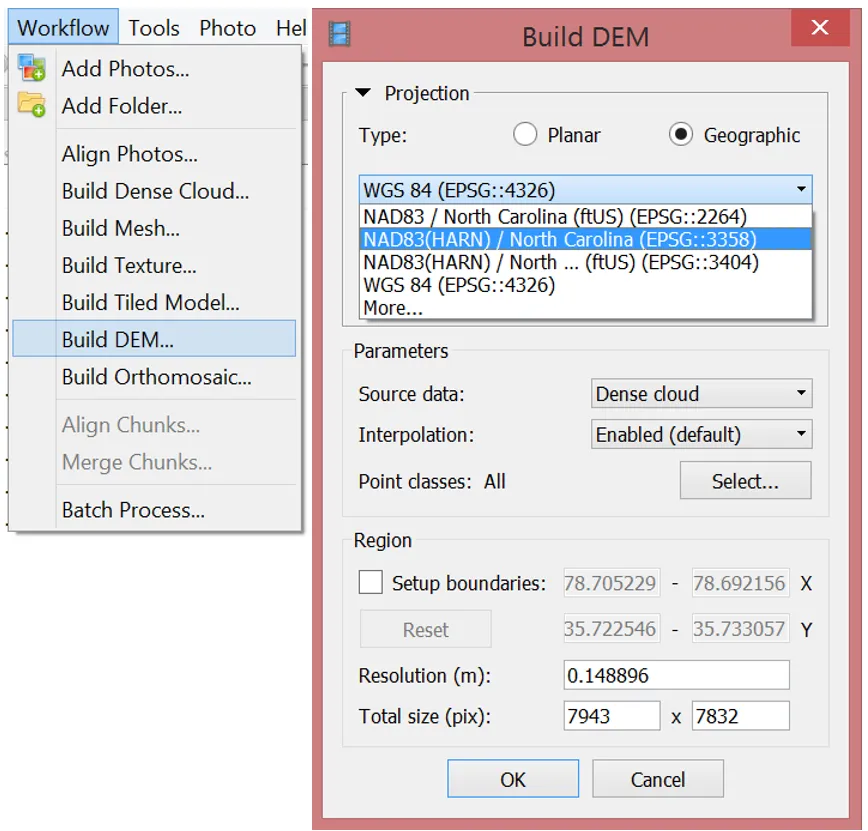
Parameters
- Source data: Dense point cloud
- Interpolation
- Disabled: leads to accurate reconstruction results since only areas corresponding to dense point cloud points are reconstructed
- Enabled (recommended): Interpolation mode - Agisoft will calculate DEM for all areas of the scene that are visible on at least one image.
Generating orthophoto
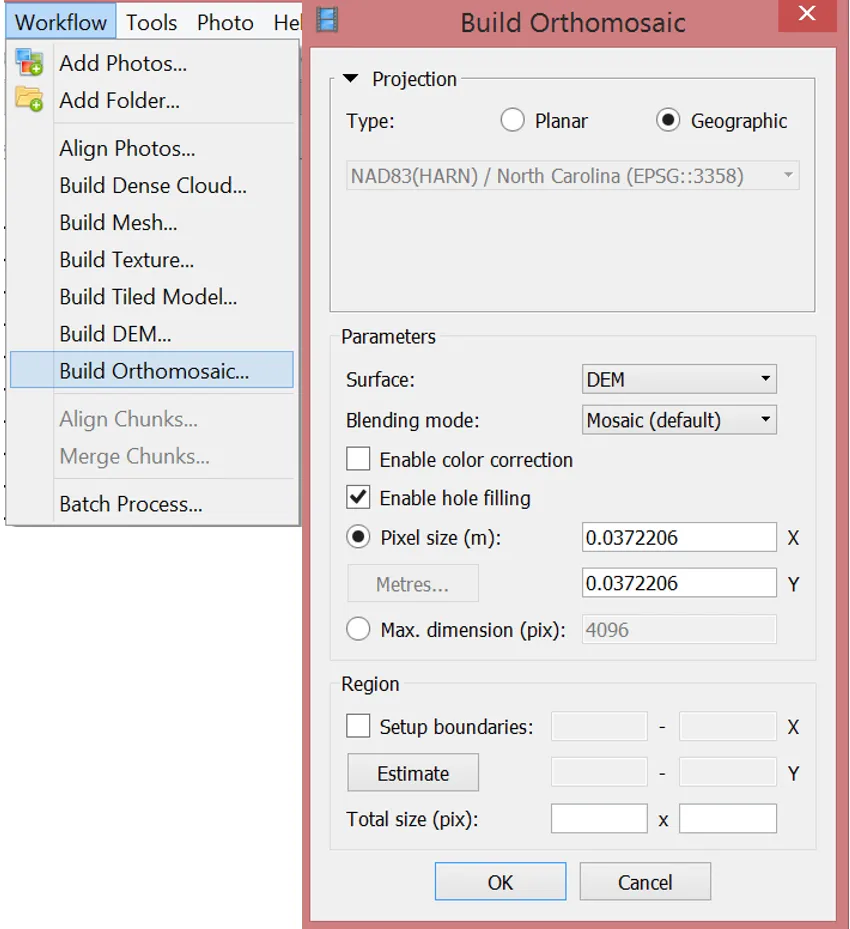
Parameters
- Surface: DEM
- Blending mode
- Mosaic (default): Implements an approach with data division into several frequency domains, which are blended independently
- Average: Uses the weighted average value of all pixels from individual photos
- Disabled: The color value for the pixel is taken from the photo with the camera view being almost along the normal to the reconstructed surface in that point.
Exporting results & saving intermediate results
Orthophoto export

Exporting results & saving intermediate results
DEM export
Exporting results & saving intermediate results
3D model export
Exporting results & saving intermediate results
Point cloud export
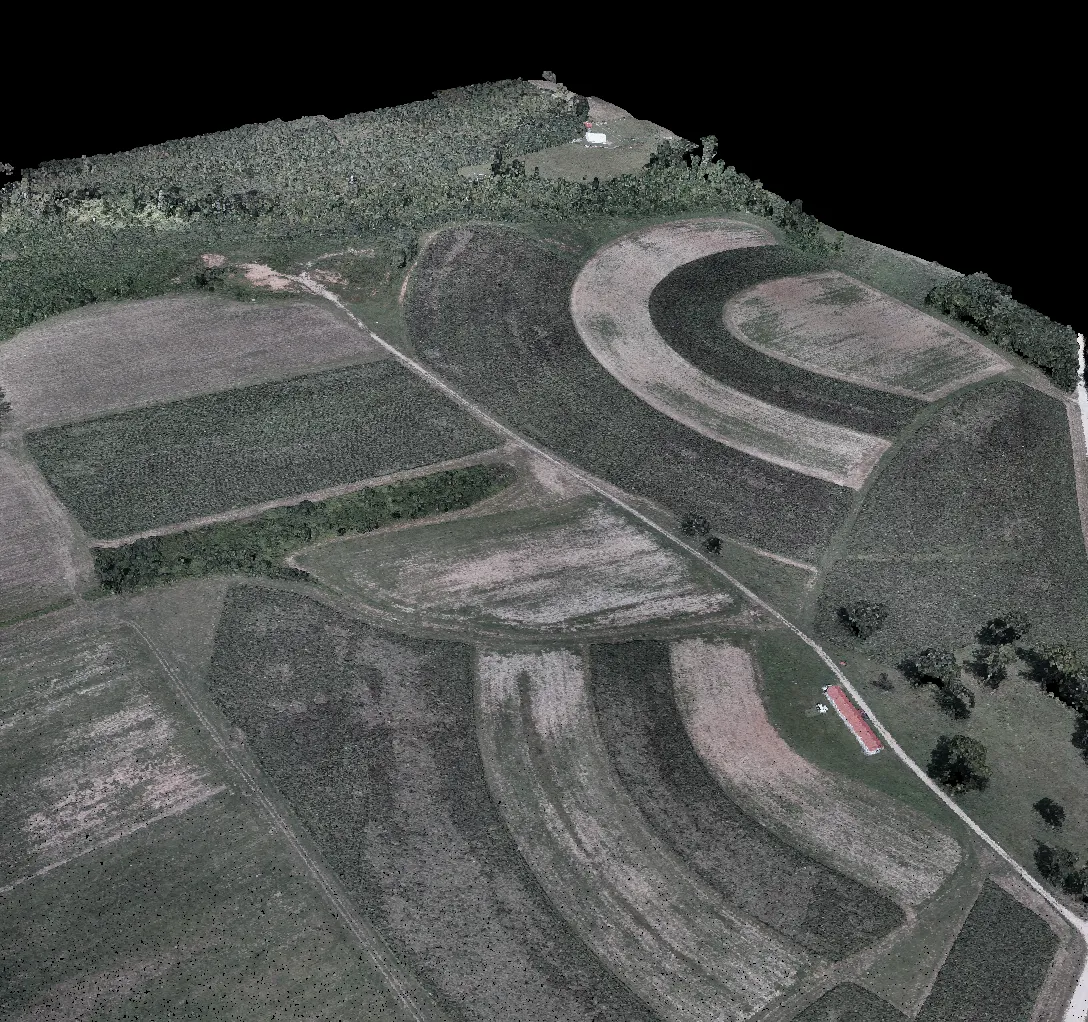

Exporting results & saving intermediate results
Processing report generation
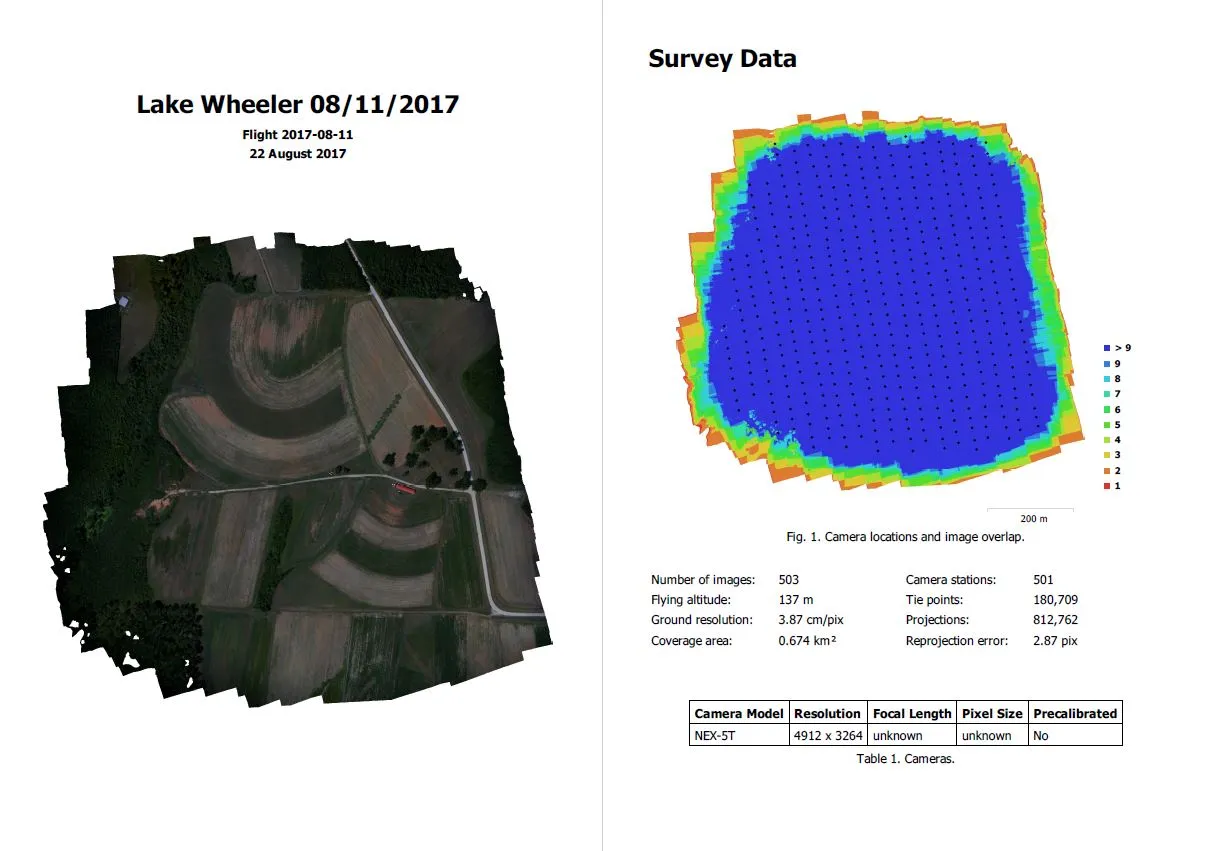
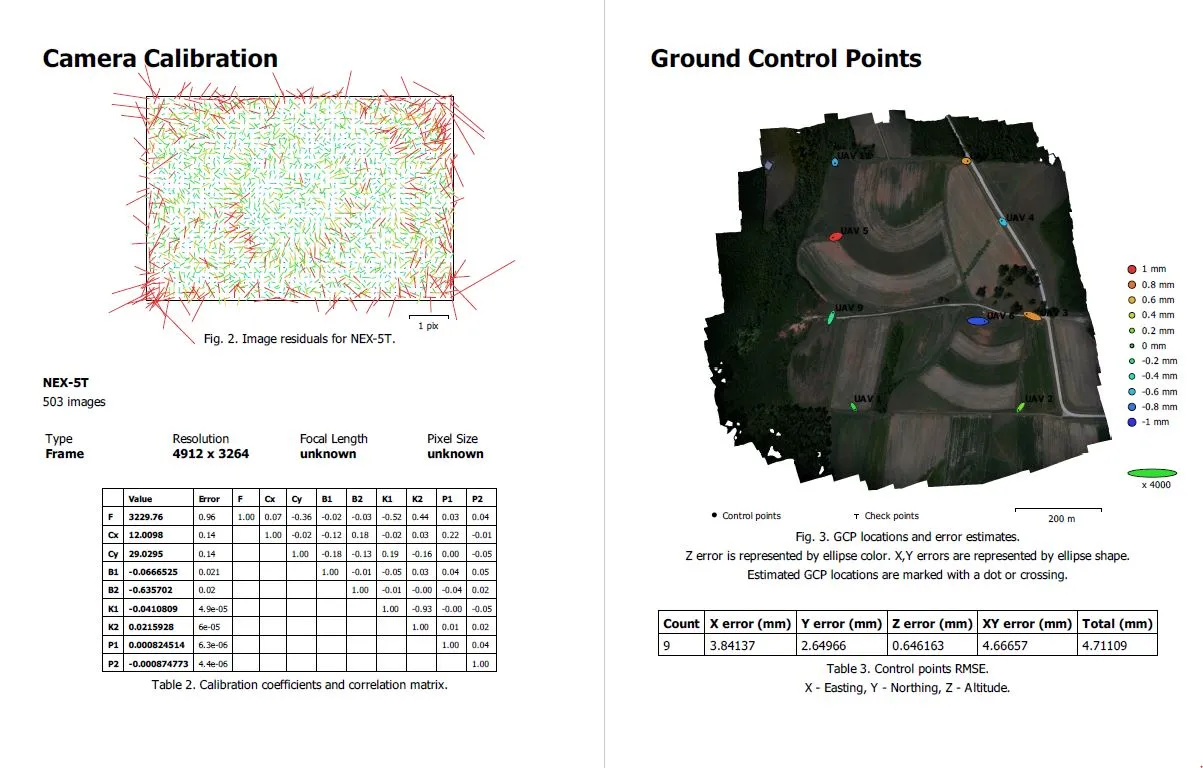
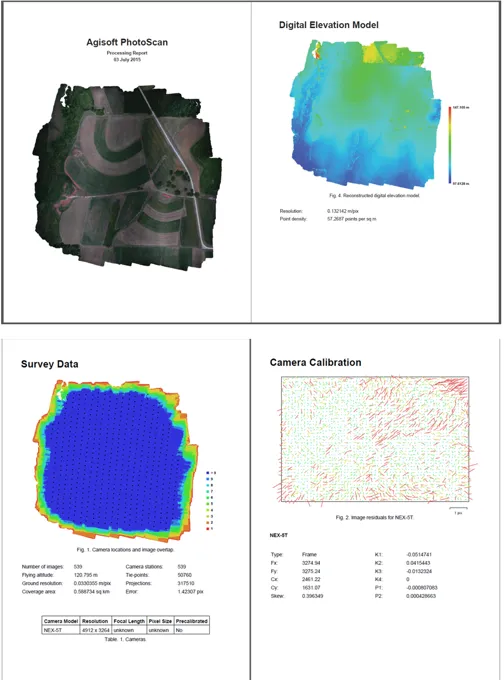
Processing report
Includes:
- Orthophoto and digital elevation model sketch
- Camera parameters and survey scheme
- Tie points data export (matching points and panoramas)
- Image overlap statistics
- Camera positioning error estimates
- Ground control point error estimates
Batch processing
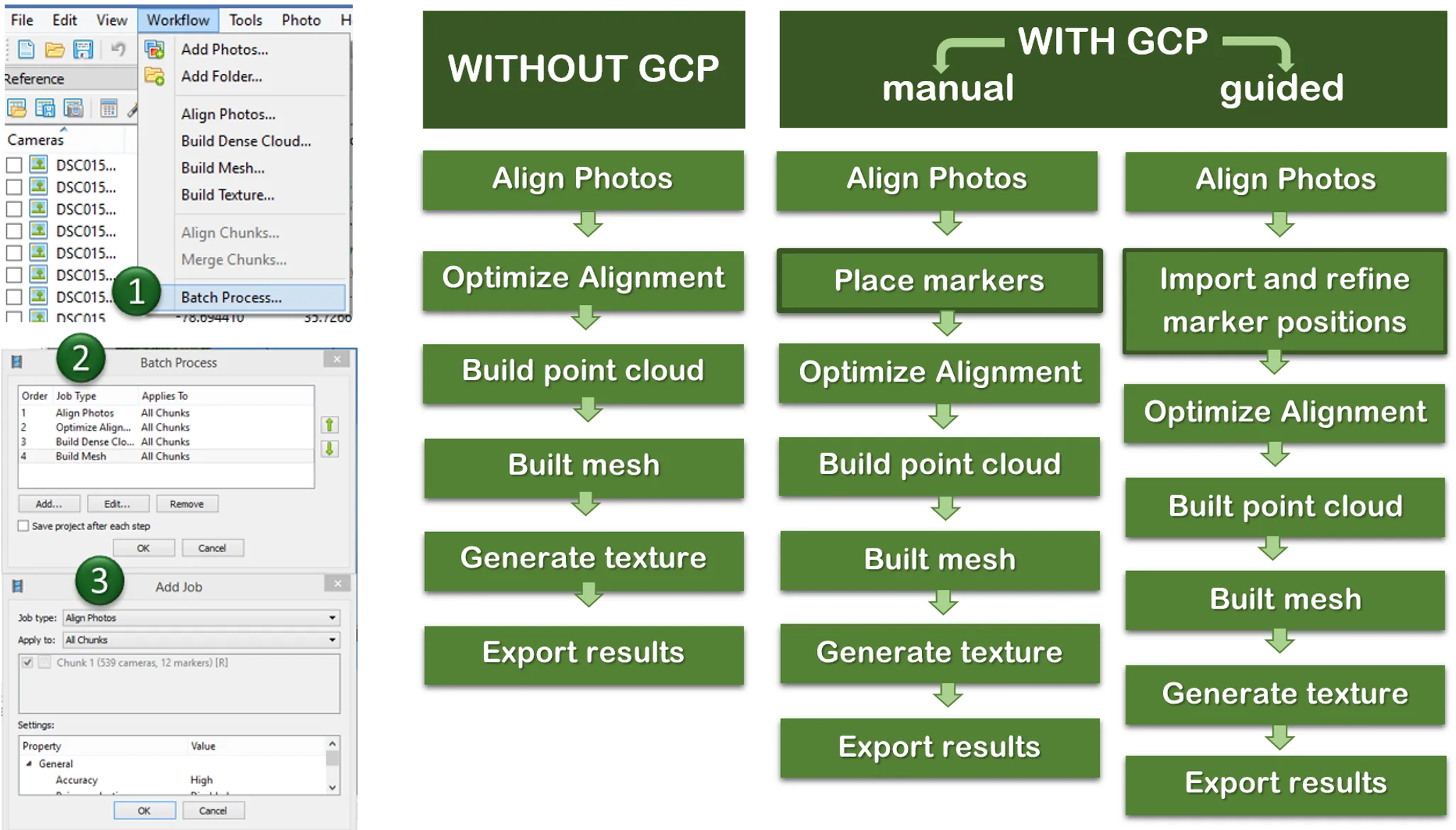
Quality processing with GCPs
- Marker positions are defined by their projections on the source photos
- After optimizing alignment based on markers, Point cloud generation and other steps need to be performed
- Used for:
- Setting up a coordinate system
- Photo alignment optimization
- Measuring distances and volumes
- Marker-based chunk alignment
- Used for:
- More on GCP placing and processing in Agisoft see intro to the assignment
What did we learn?
- What is a general workflow for UAS imagery processing
- How do we transform UAS data into orthophoto, DSM, 3D model, and point cloud
- How to process the data in Agisoft Metashape Professional and how to set proper parameters in the program
