Obtaining good quality UAS data
UAS Operations and Analytics Workshop
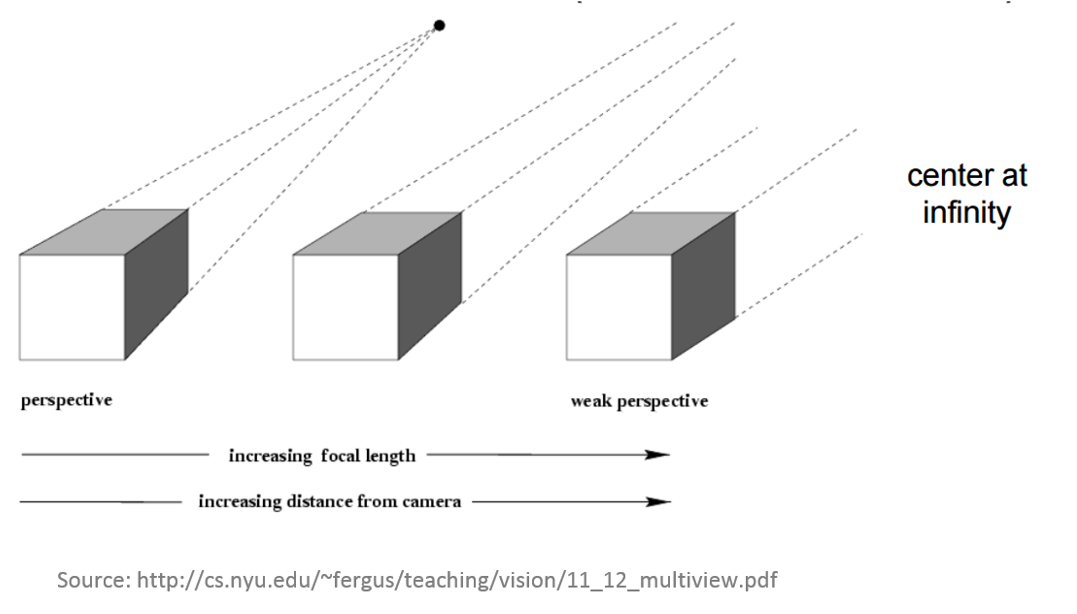
Photogrammetric process
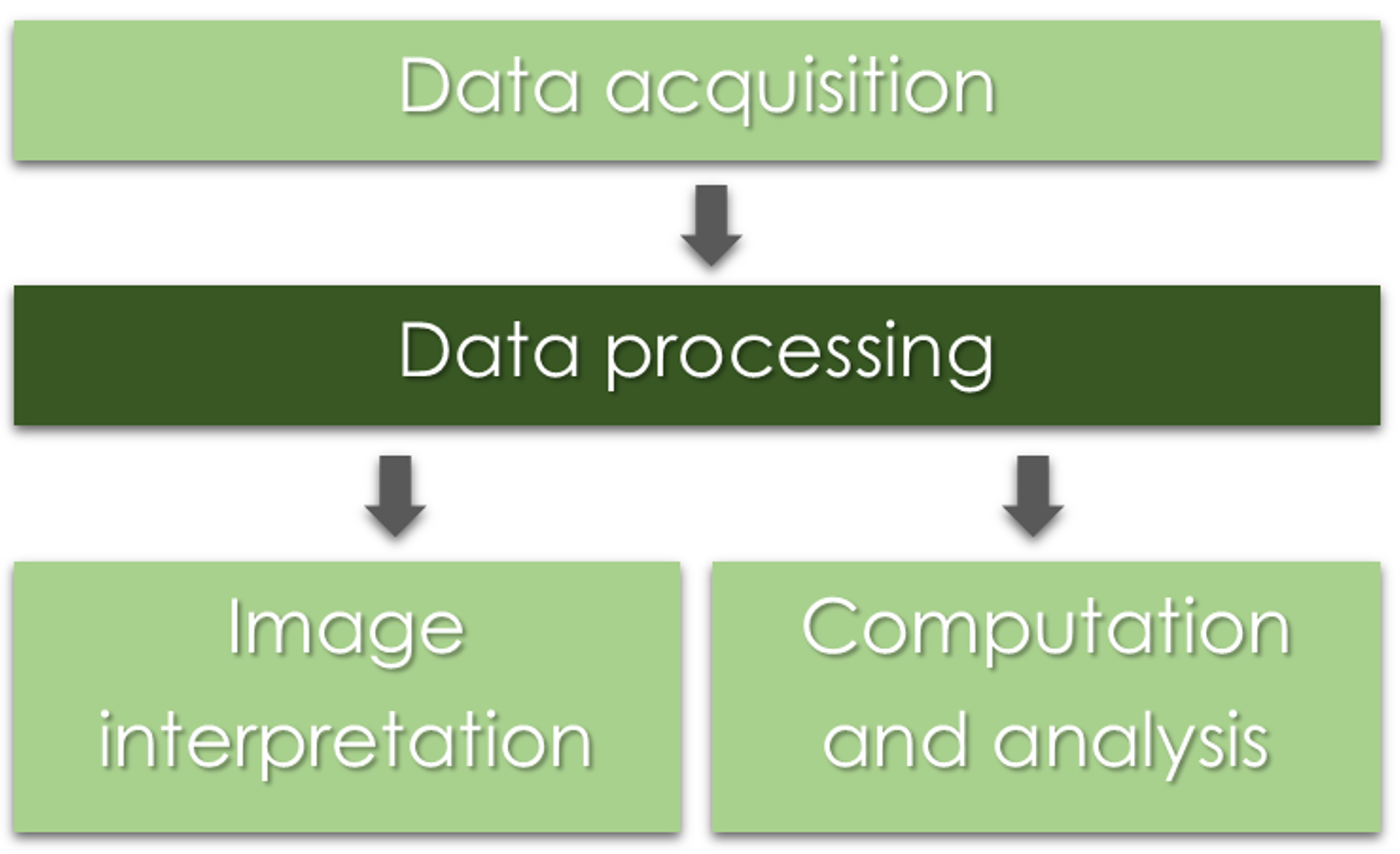
UAS Photogrammetric process
Throughout the whole process, it is important to remember
- What is the aim or the project? and
- What will be the data used for?
What do we need?
- Digital imagery;
- (Digital elevation model or topographic dataset)
- (Exterior orientation parameters from aerial triangulation or IMU);
- (Camera calibration report);
- (Ground Control Points parameters);
- Photogrammetric processing software that utilizes collinearity equations.
What do we need?
- Digital imagery;
- .
- ..
- .
- .
- Photogrammetric processing software that utilizes collinearity equations.
Multiple-view geometry questions
- Scene geometry (structure):
Given 2D point matches in two or more images, where are the corresponding points in 3D? - Correspondence (stereo matching): Given a point in just one image, how does it constrain the position of the corresponding point in another image?
- Camera geometry (motion): Given a set of corresponding points in two or more images, what are the camera matrices for these views?
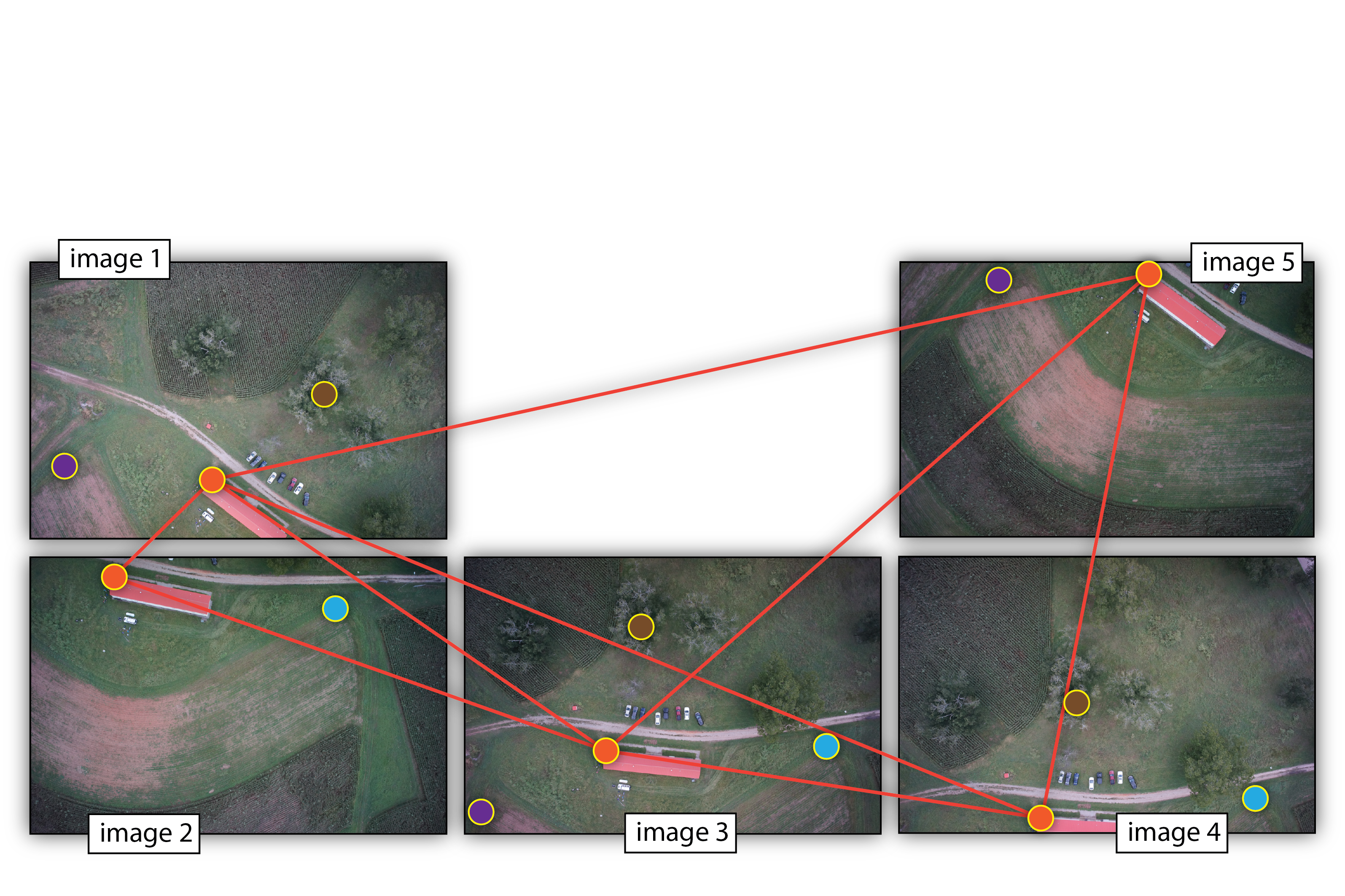
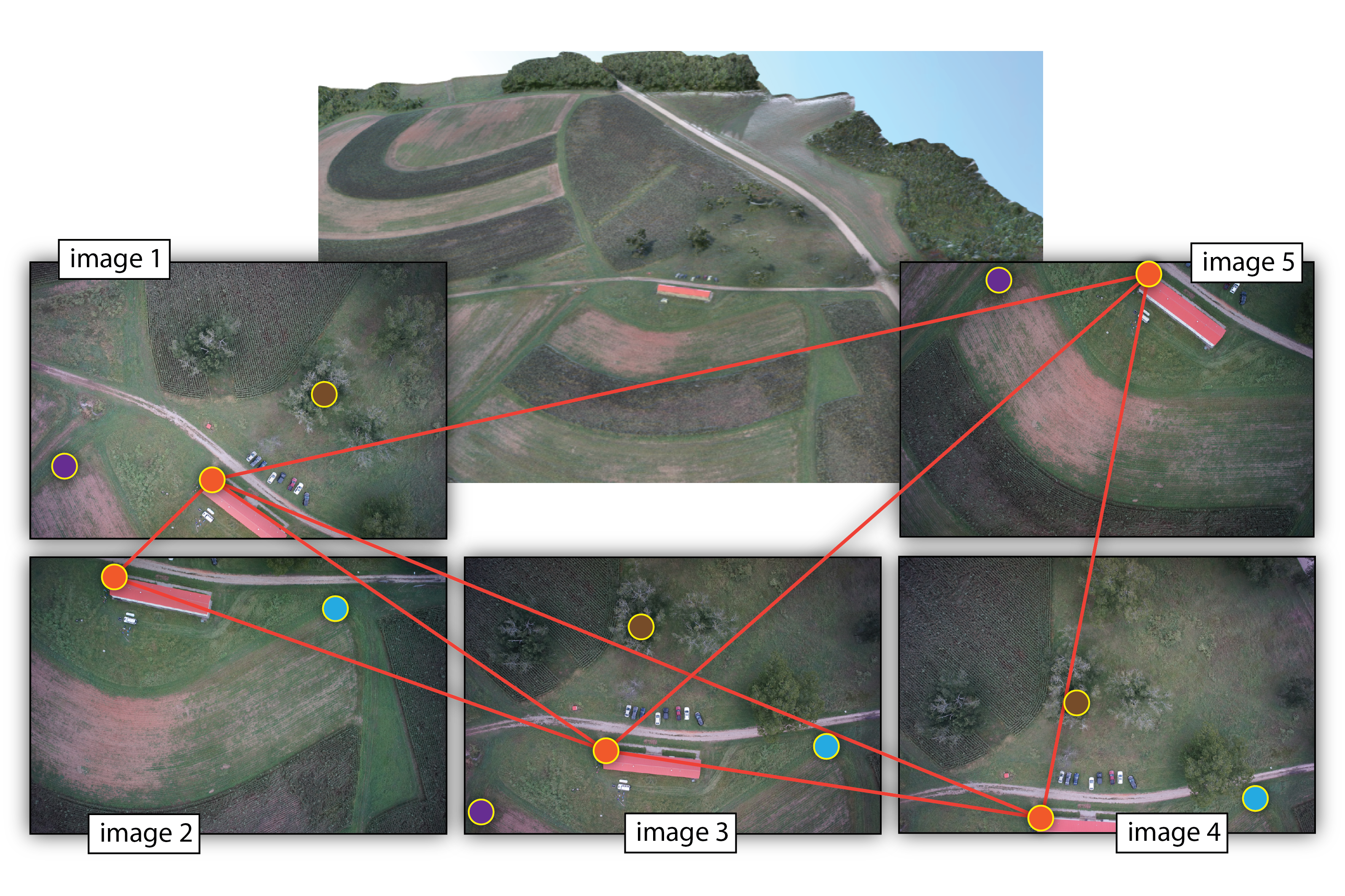
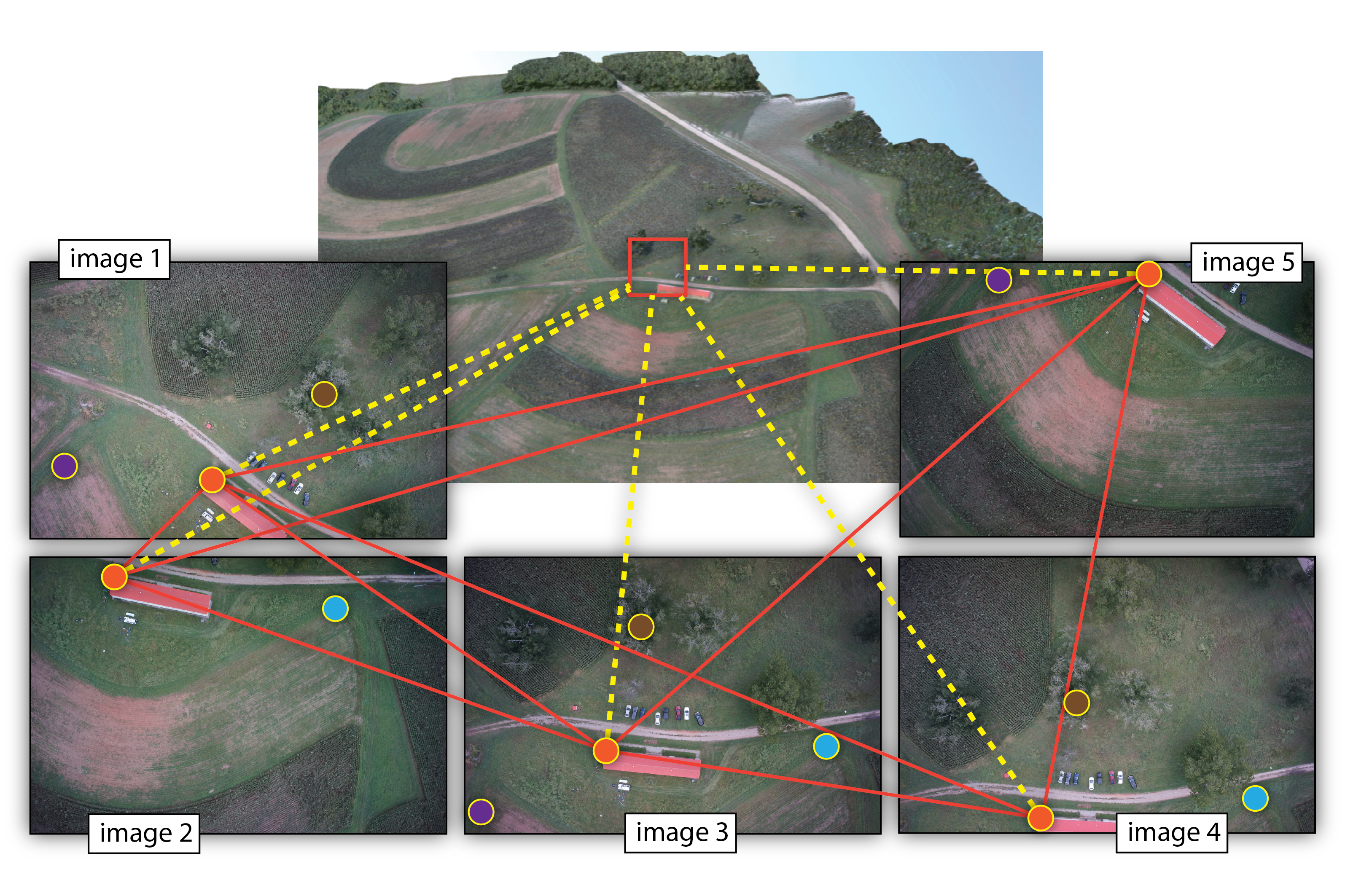
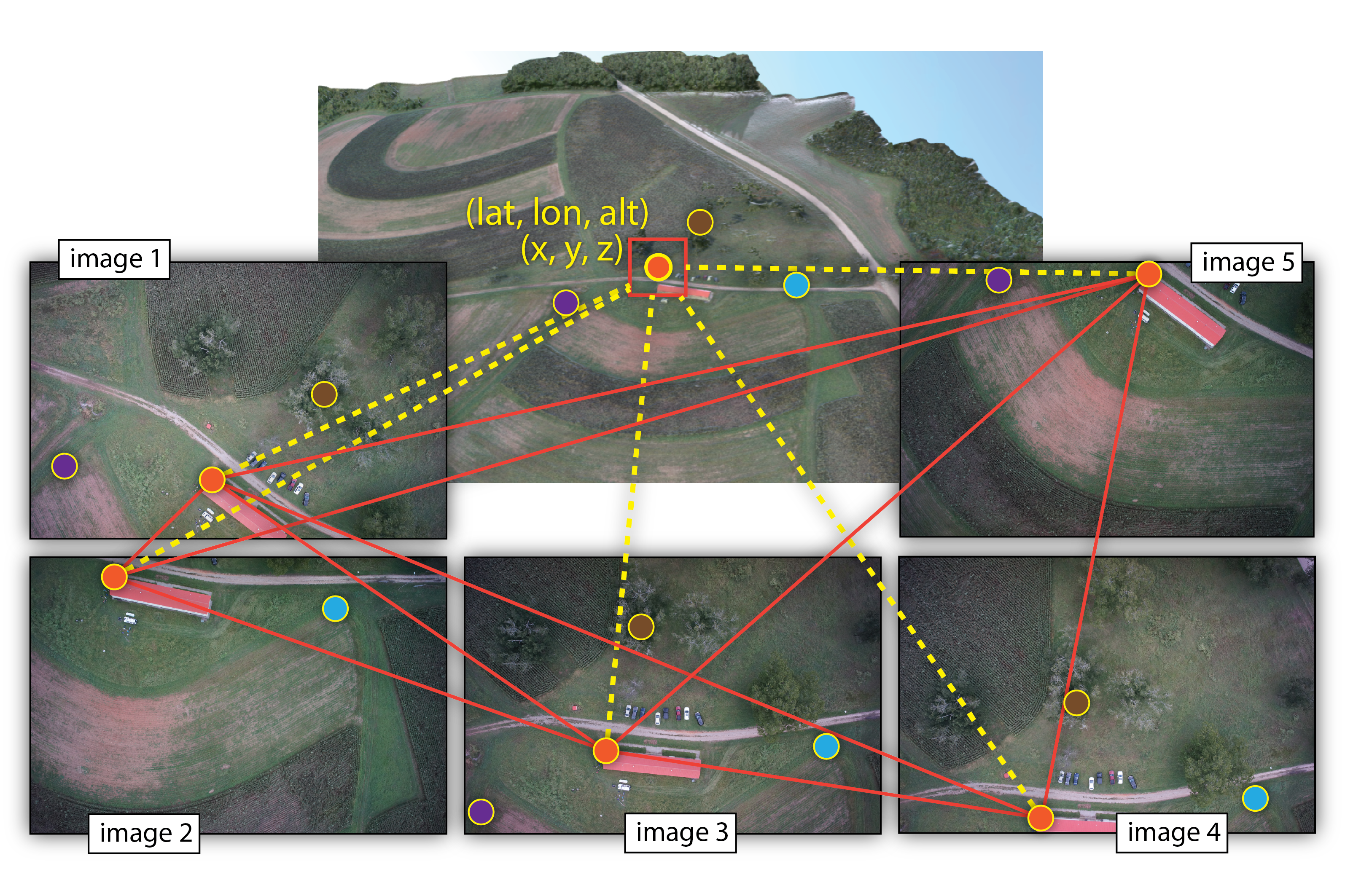
Structure from Motion (SfM)
- range imaging technique,
- process of estimating 3D structures from 2D image sequences,
- may be coupled with local motion signals
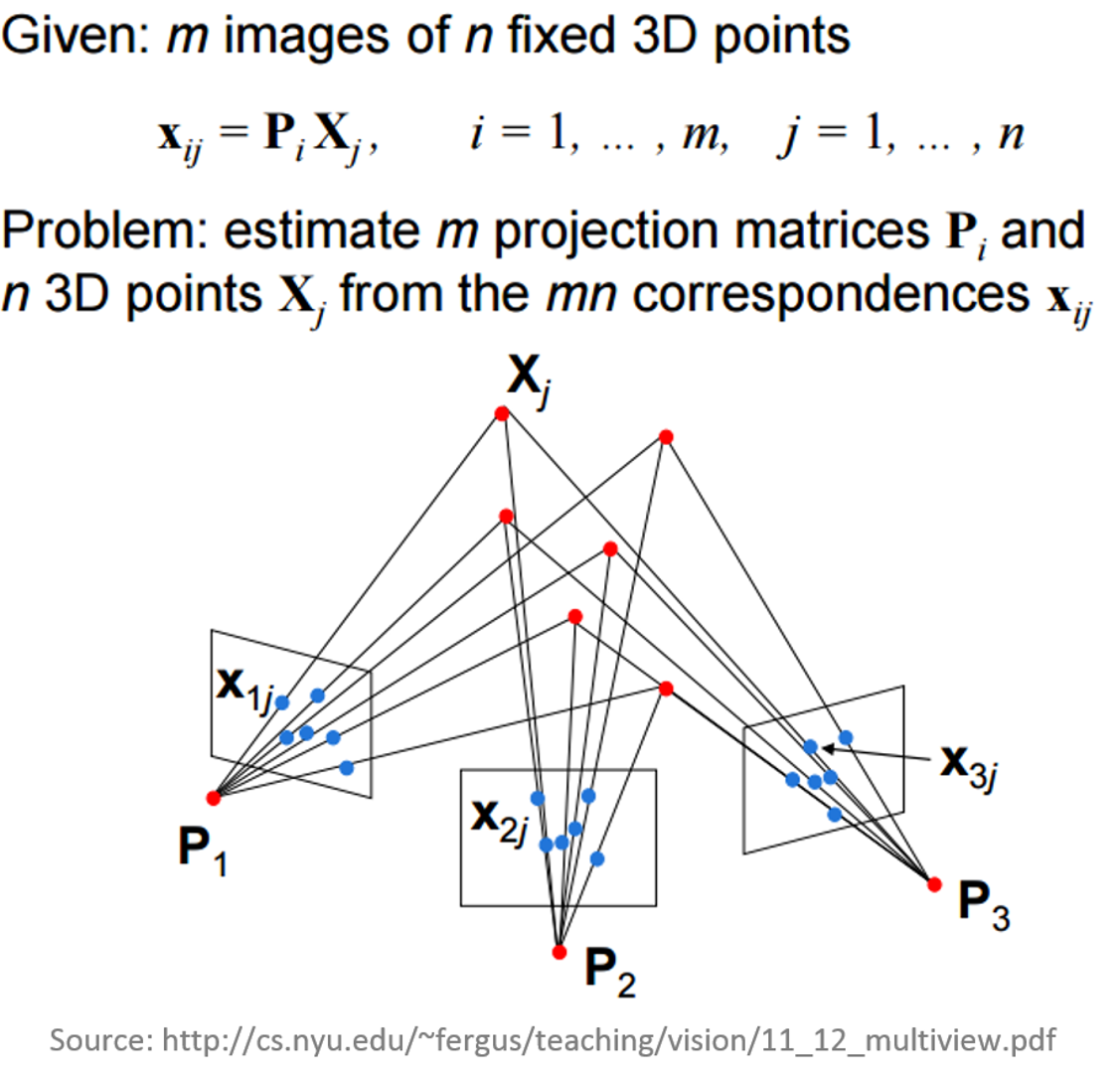
Structure from Motion (SfM)

Structure from Motion (SfM)

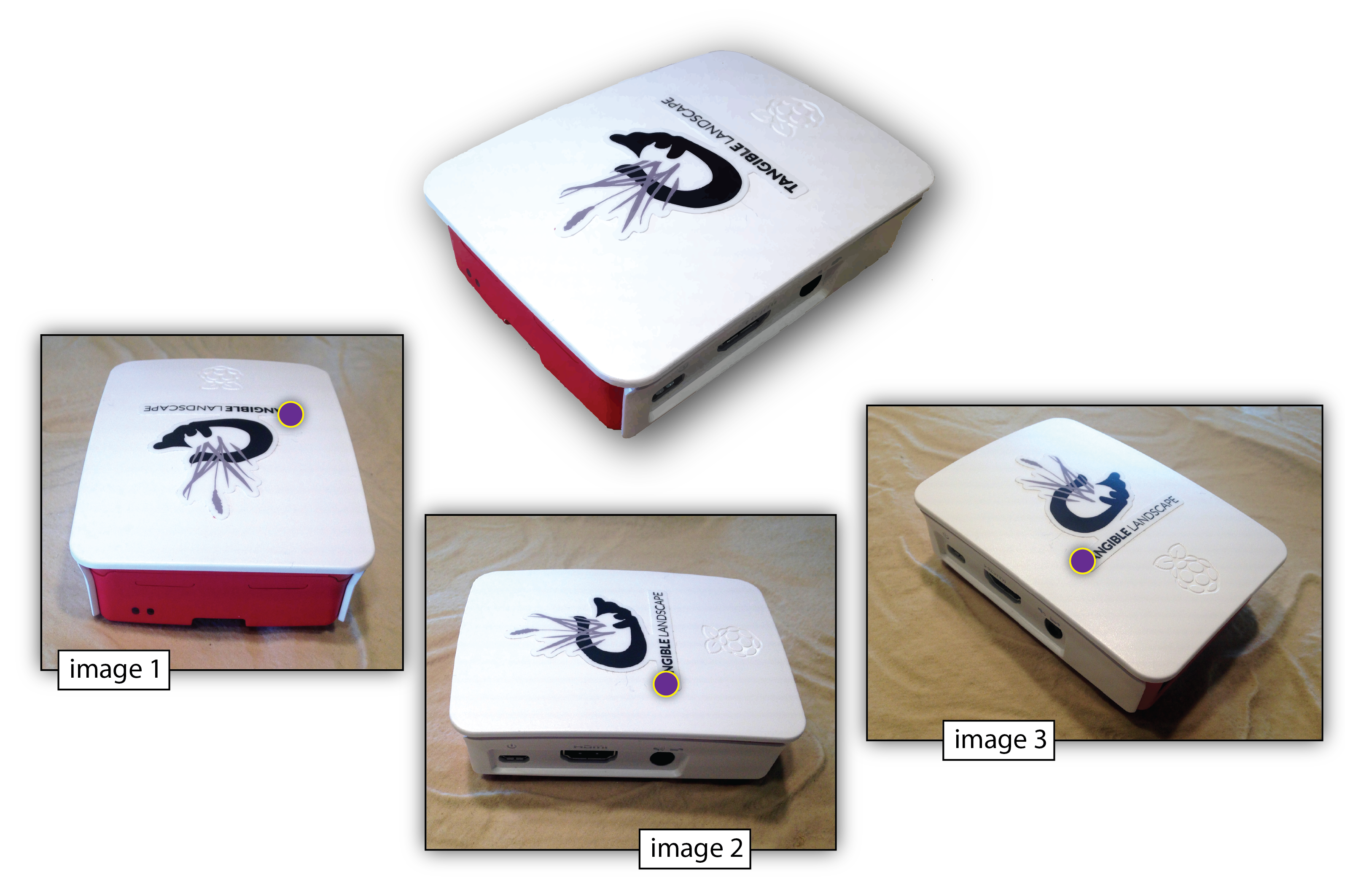
Structure from Motion (SfM)

Structure from Motion (SfM)
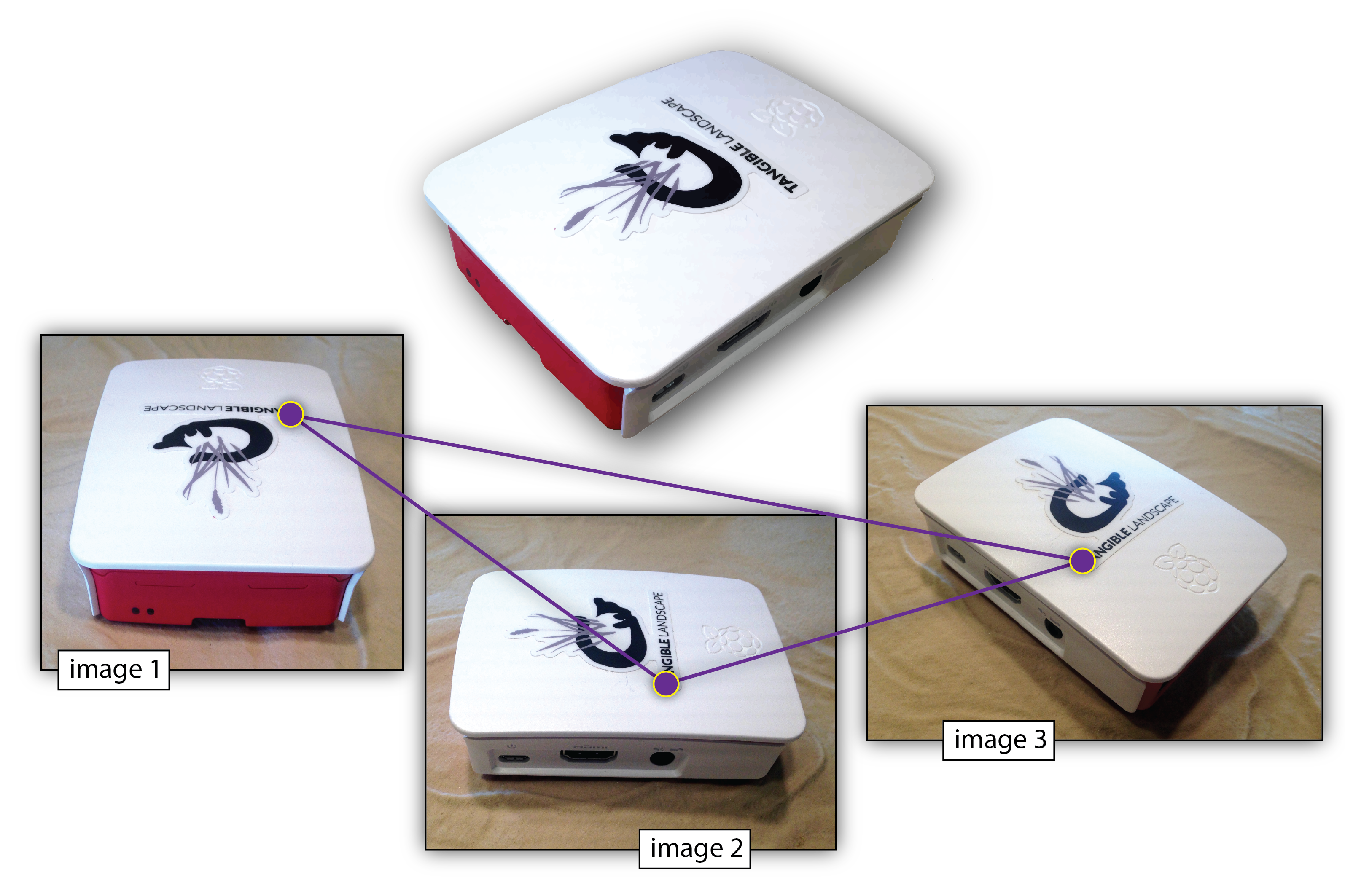
Structure from Motion (SfM)
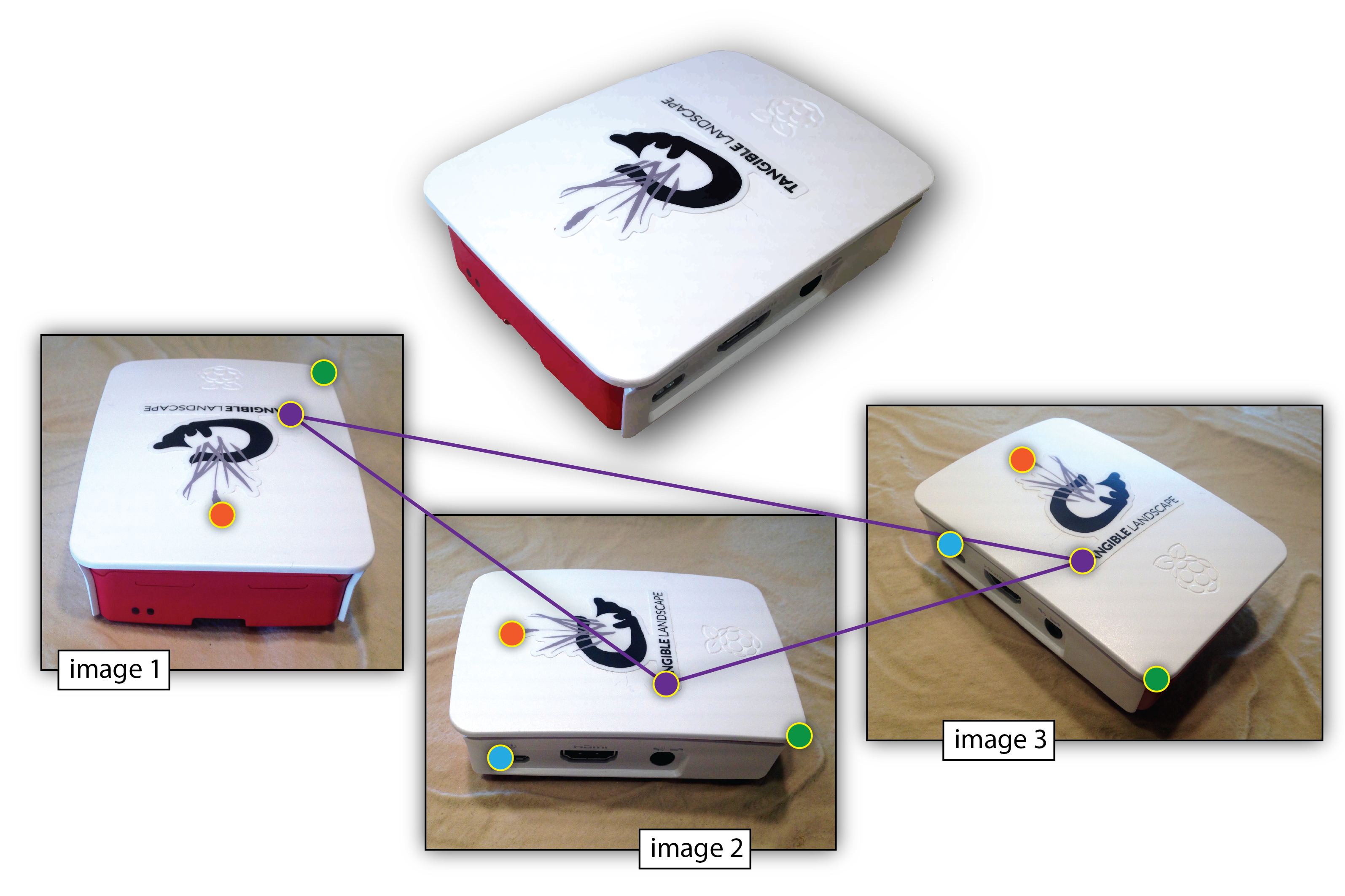
Structure from Motion (SfM)
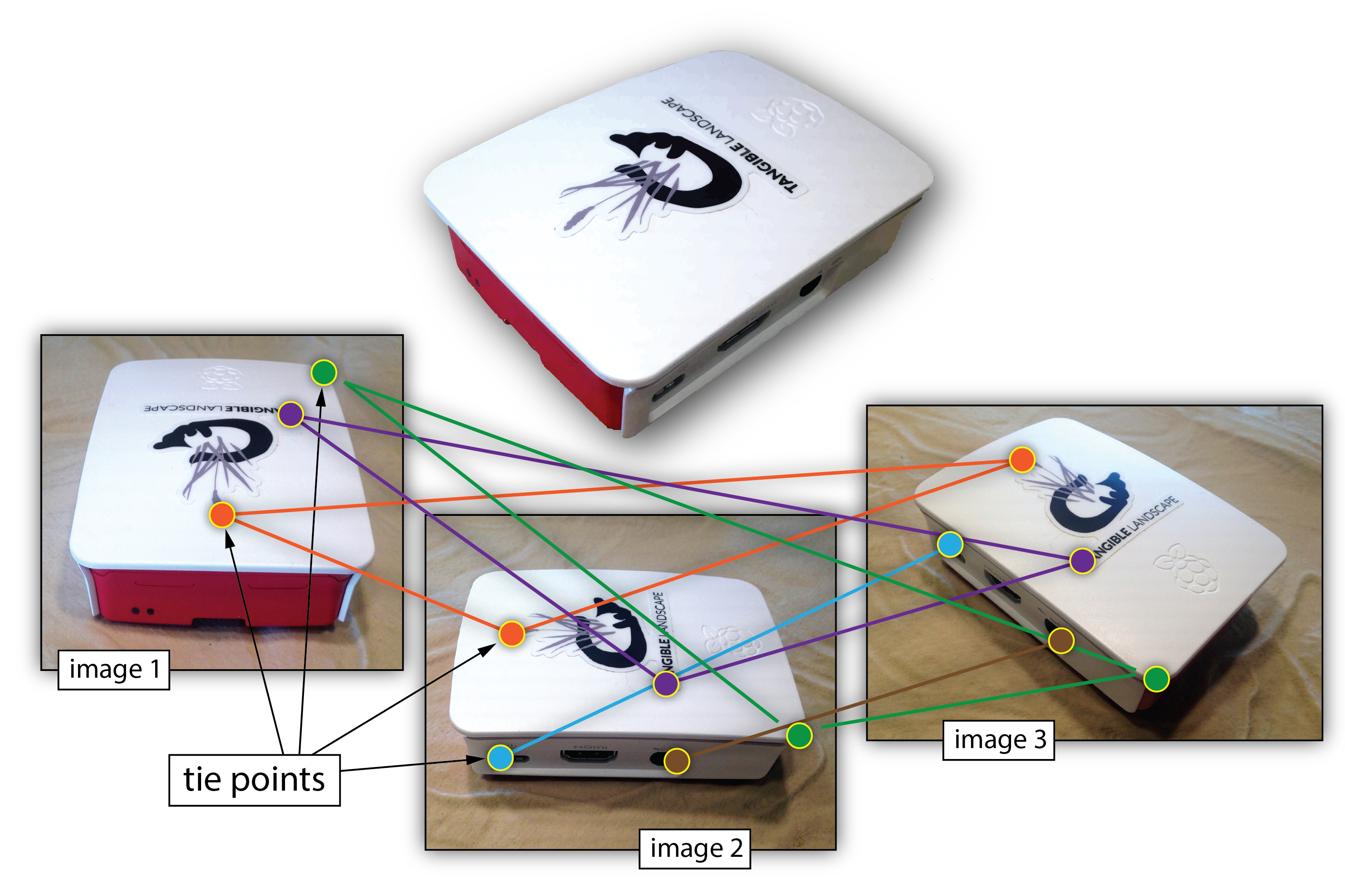
Structure from Motion (SfM)
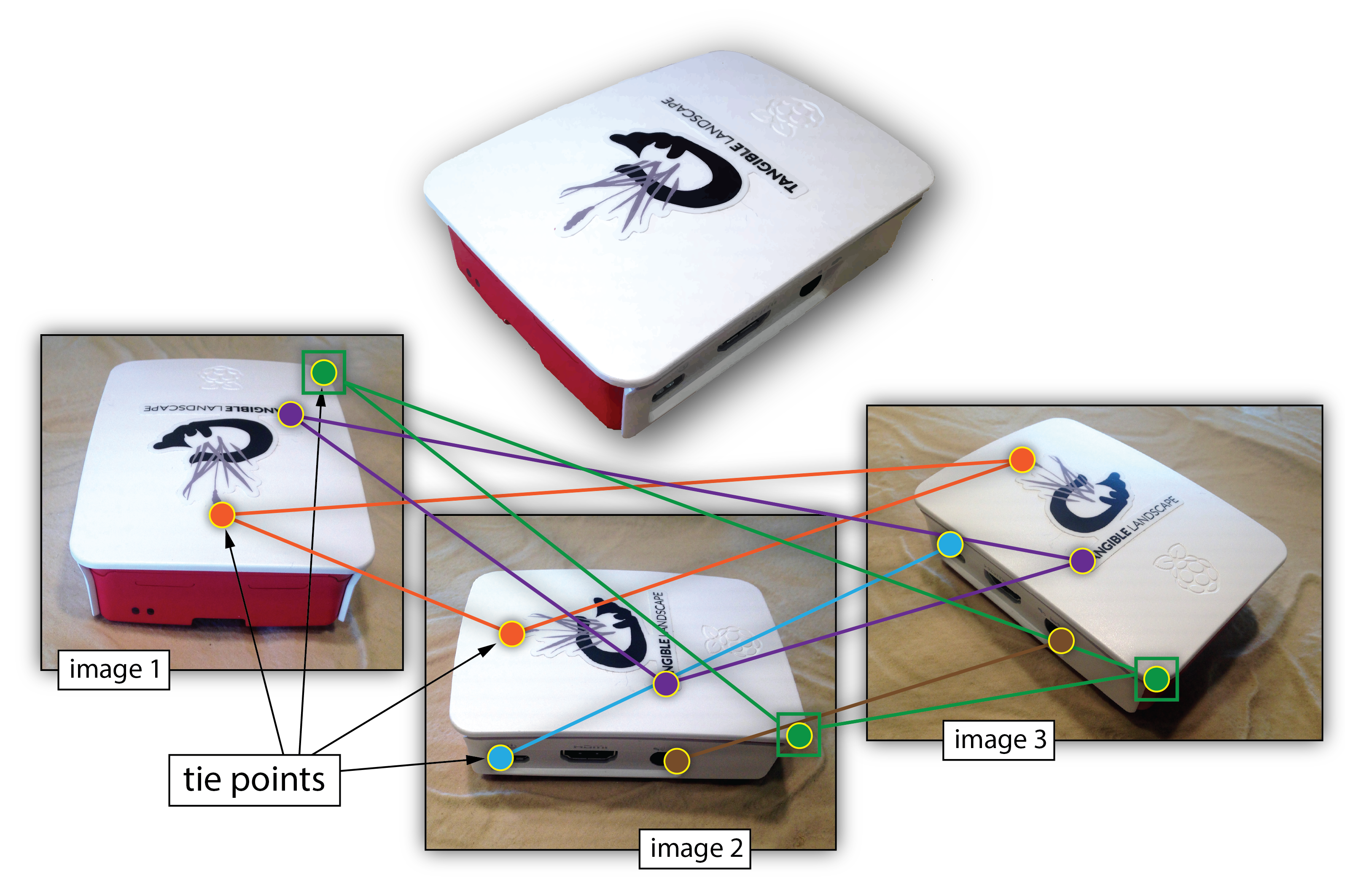
Structure from Motion (SfM)
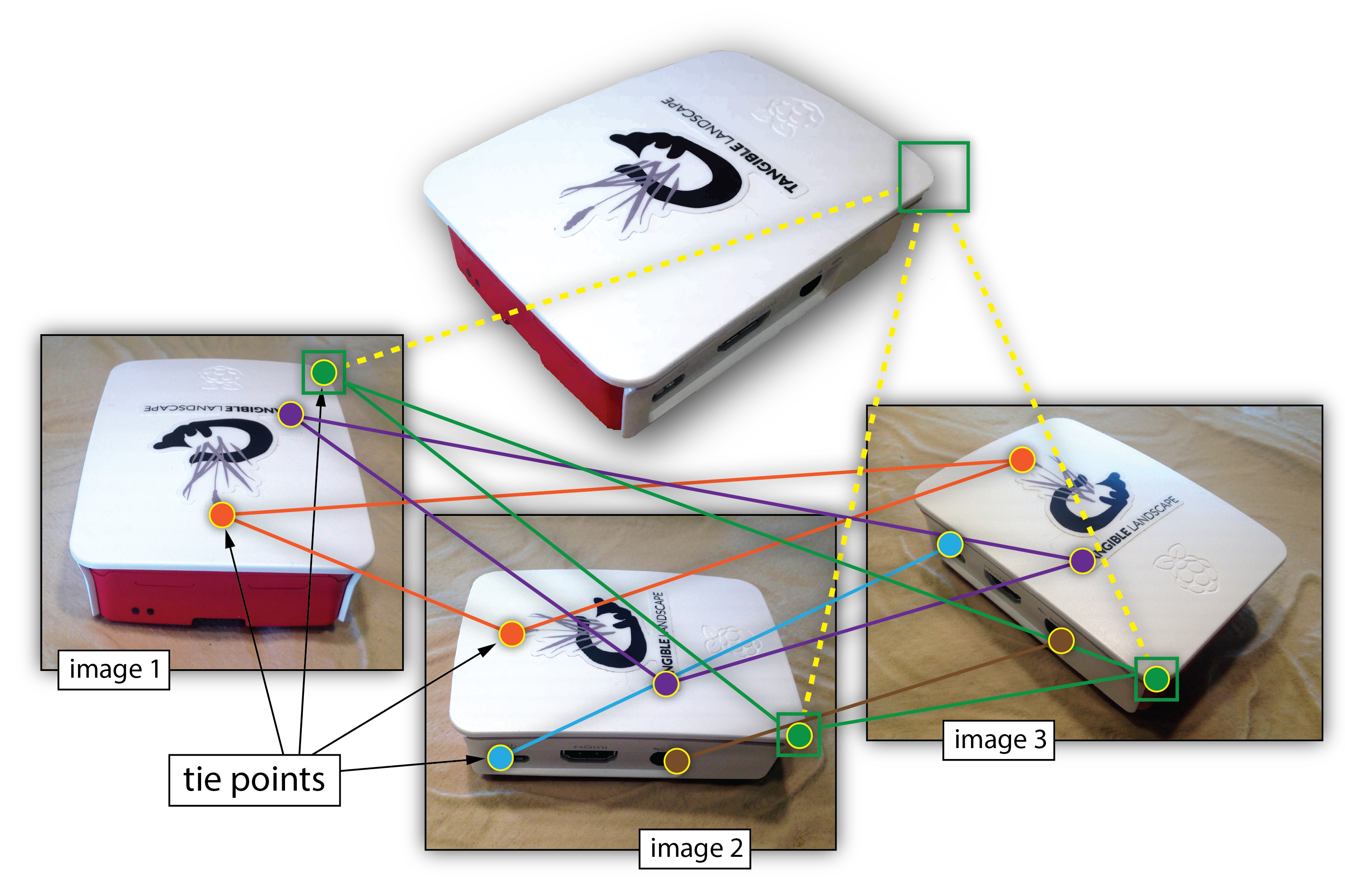
Structure from Motion (SfM)
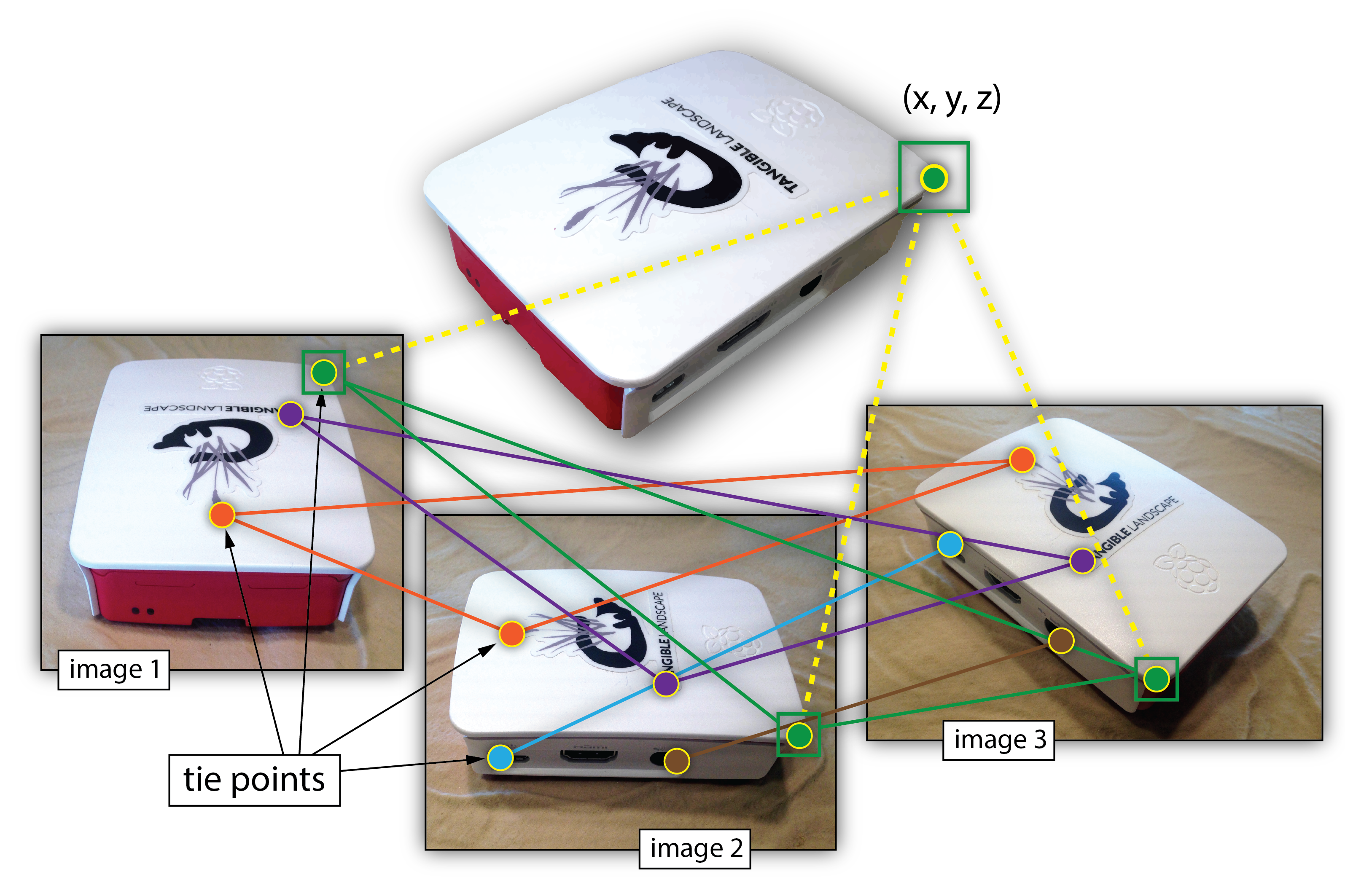
Structure from Motion (SfM)

Structure from Motion (SfM)

Structure from Motion (SfM)
Structure from Motion (SfM)
Structure from Motion (SfM)
Structure from Motion (SfM)
What do we need?
- Digital imagery;
- (Digital elevation model or topographic dataset)
- (Exteriororientation parameters from aerial triangulation or IMU);
- (Camera calibration report);
- (Ground Control Points parameters);
- Photogrammetric processing software that utilizes collinearity equations.
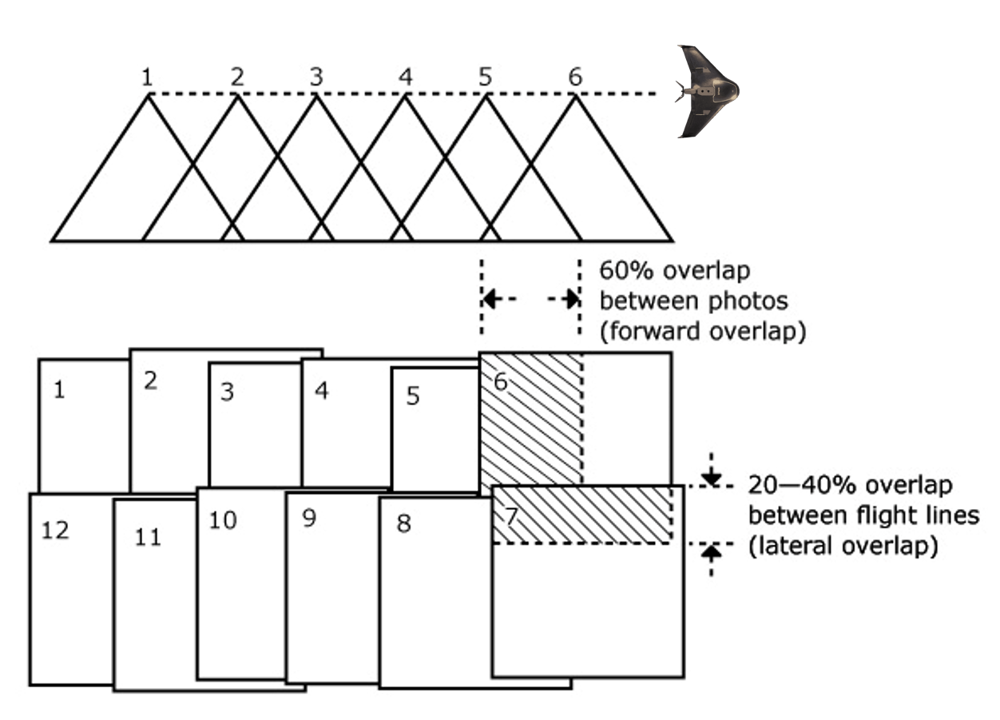
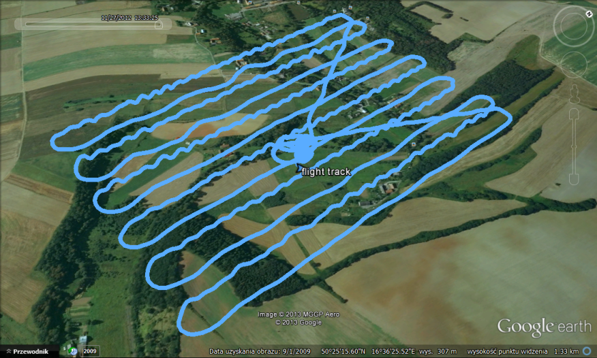
1. Digital imagery


Aerial survey
What do we need?
- Digital imagery;
- (Digital elevation model or topographic dataset)
- (Exteriororientation parameters from aerial triangulation or IMU);
- (Camera calibration report);
- (Ground Control Points parameters);
- Photogrammetric processing software that utilizes collinearity equations.
5. Ground Control Points
- GCP - target in the project area with known 3 coordinates (X,Y,Z or lat, long, alt)
- Accurate, well placed and marked GCPs are essential elements for model accuracy and georeferencing
Photo Identifiable (Photo ID):
- any feature on the ground,
- specific (e.g. corners)
- unmovable,
- not covered by vegetation
- it can be surveyed later on.
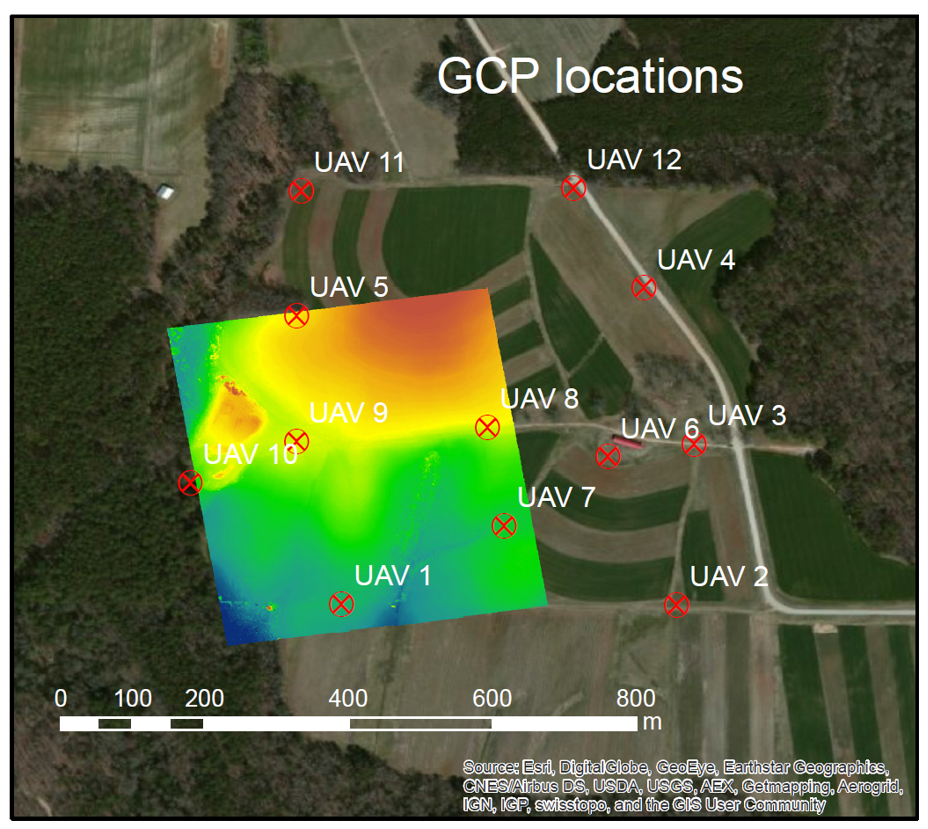
Ground Control Points
Pre-marked (Panels): marking or painting figures or symbols on the ground before the UAS flies


Why Ground Control Points?
- necessary for georeferencing if photos are not geotagged
- improve precision of the model
- useful for quality control